Lexus models, including the LS sedan, RX crossover and GX SUV, are some of the least problematic air ride vehicles on the road. In fact, most Lexus customers do not realize that their vehicle is equipped with an air suspension until something breaks.
Like all air ride systems, if you are not familiar with the system operation, you can throw a lot of parts at it without achieving any results. Taking some time to look at the theory and operation sections of the service information can save you a lot of lost time speculating on the source of the problem.
Basics
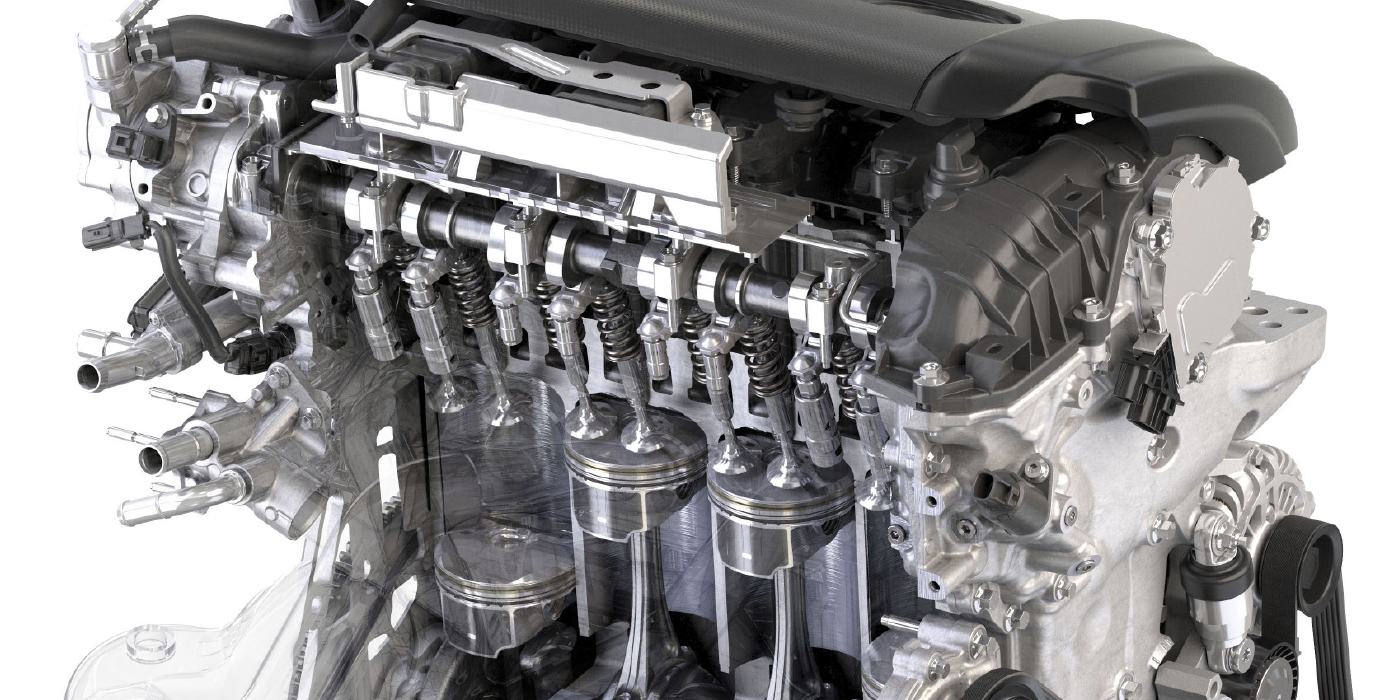
What makes most Lexus systems unique is the lack of a reservoir. The compressor provides air “on-demand.” Most systems will use four ride height sensors that measure the height and speed of the wheel displacement. The suspension control ECM will filter the ride height readings and other sensor data from accelerometers, and even data from the engine ECU, to determine which air spring intakes air or exhausts it. The suspension control ECU will also adjust the valving of the dampeners for the best possible ride.
The air ride system is tied into the active dampening system. The system optimizes the spring rates of the bladders and the compression/rebound settings of the dampeners. It does this very quickly and can react to bumps and body movement. The driver can select sport, comfort and normal modes. The driver can also select the high and normal modes for the air suspension. In normal mode, the ride height is optimized for the road surface and vehicle speed.
If you are jacking up the vehicle, Lexus recommends that the engine be off, on some models, so the system will not attempt to trim the suspension. If the vehicle must be raised with its engine running, connect terminals 11 and 4 of the OBDII connector to stop the vehicle height control operation of the suspension control ECU.
Diagnostics & Sensors
When diagnosing any Lexus air ride system, it is advisable to have a scan tool that can communicate with the Suspension Control ECU, and also bi-directionally control the modules, actuators and valves. Not having an enhanced scan tool with these functions can severely handicap any air ride repair. It is also required to calibrate the ride height sensors.
The system uses four ride height sensors, as mentioned earlier. It also uses acceleration sensors to measure body movement. These sensors are mounted under the instrument cluster and in the trunk on the passenger’s side. They measure how the road surface is causing the body to move. Other inputs from the ECU, Body ECU and other modules on the CAN bus are used by the Suspension Control ECU.
Through the four ride height control sensors, the Suspension Control ECU detects changes in the vehicle height that result from the number of occupants or the amount of the load. Then, the Suspension Control ECU controls the height control solenoid valves, the compressor and motor with the dryer to automatically adjust the vehicle height to a constant level.
Diagnosing these sensors is straightforward and typically requires only a scope and meter. The ride height Hall Effect sensors have three wires for ground power and signal. You can test the accelerometers by checking the signal voltage and tilting the sensor. But, the best way to test them is to observe their outputs through a scan tool.
Topology
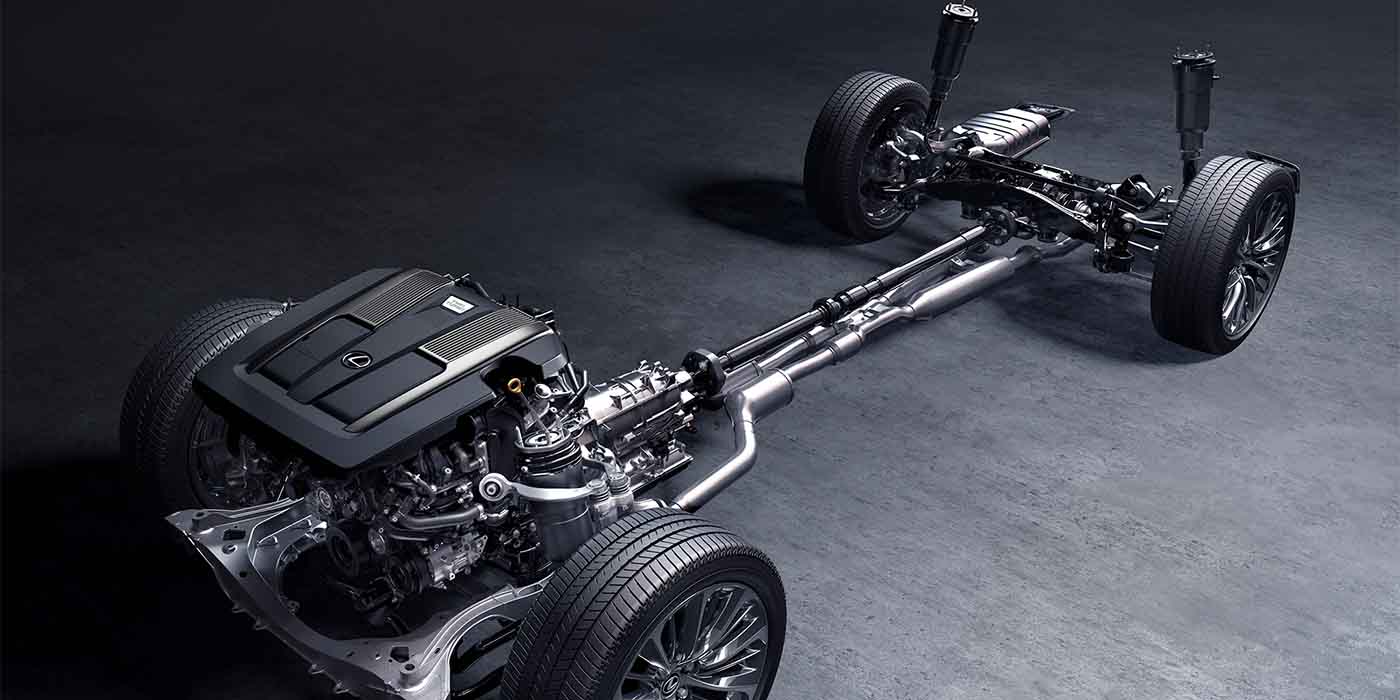
The Suspension Control ECU operates on the CAN bus. The height and acceleration sensors are directly connected to the Suspension Control ECU. The controls for the compressor and the fill and exhaust valves are located on the control side. The system is also directly connected to the actuators that control the dampeners.
Inspecting and Testing the Dampeners
Motors that control the valving inside the unit are located on top of the struts. These units are prone to damage if they are abused or the hood is shut with an object on top. You can remove the actuators from the strut and observe movement in the motor when the modes are changed from the driver’s seat.
It is possible to manually change the actuator setting on top of the struts by grabbing onto the bar inside the shaft. There are five settings, which change for every 30 degrees of rotation. Compress the strut to see if the amount of force changes after making an adjustment.
Air Compressor and Bladders
A compressor behind the front bumper supplies the compressed air. There are two lines for the front struts on the compressor. One line goes to the rear and connects to a combination valve that contains the valves for the rear bladders. The Lexus system does not use a reservoir to trim the suspension.
Calibration and Adjustment
One of the more difficult tasks on the LS and GX SUV air suspension is adjusting the ride height after installing parts. Trying to adjust the linkages will not work. The only way to adjust the height is by using a scan tool and inputting the ride height measurements.
Conversion Kits
Considering the complexity of some Lexus air ride systems, repair of the system may not be economically viable for the customer. Some companies are offering conversion kits that switch the vehicle to a conventional system with passive hydraulic units and springs.
With some replacement compressors on upper-trim-level Lexus models costing more than $1,200, a conversion kit might cost less and provide better long-term results for the customer.