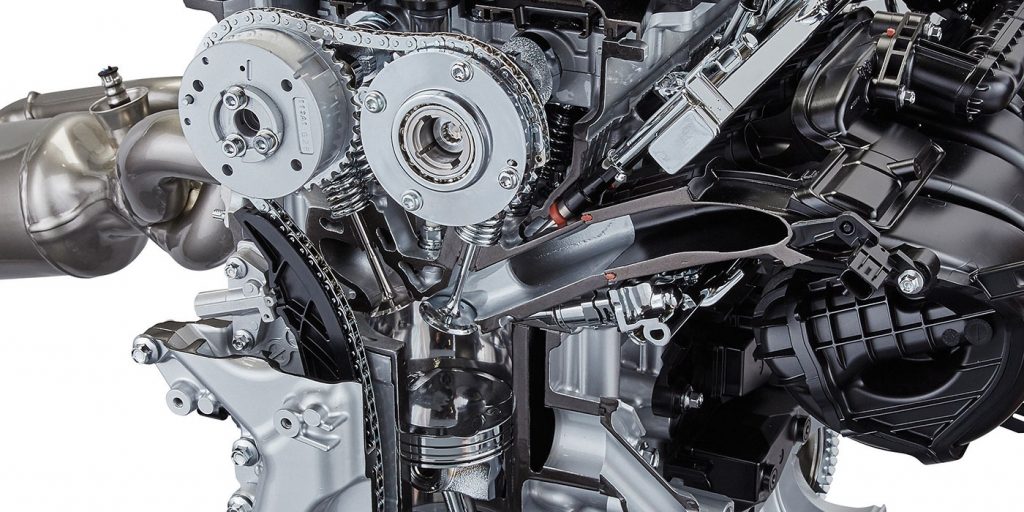
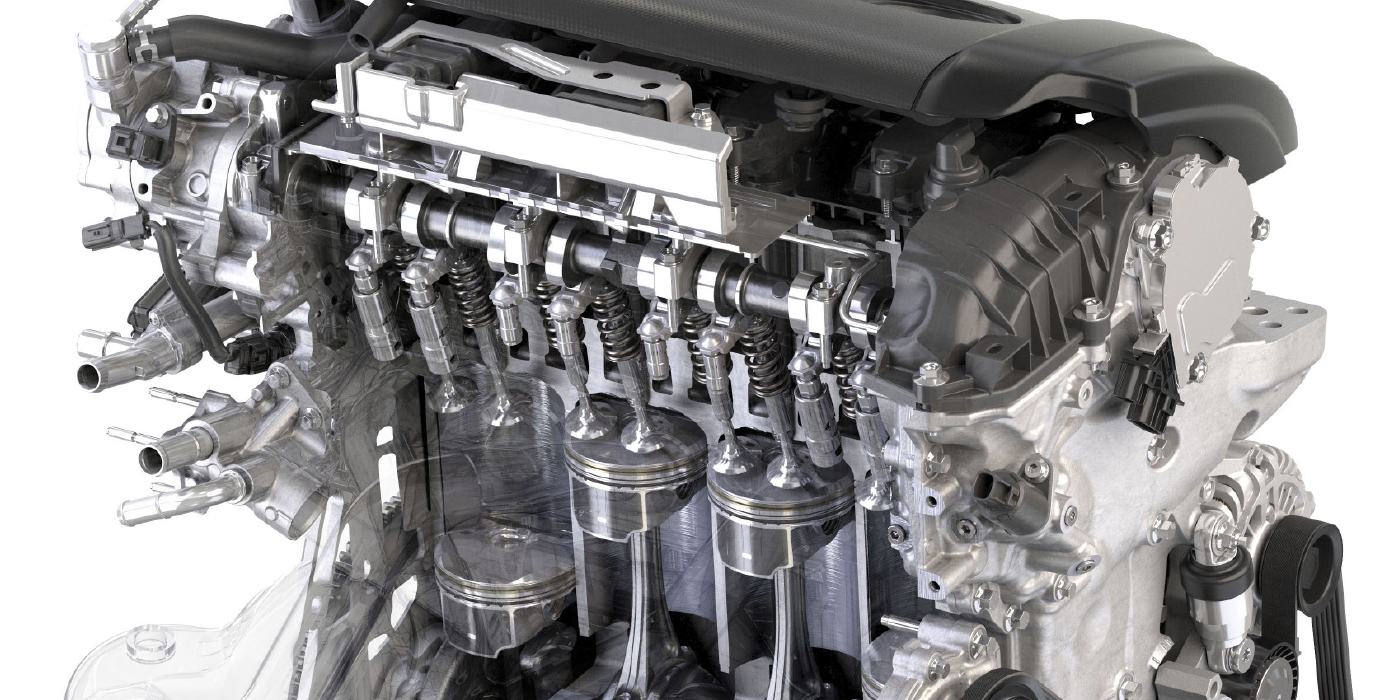
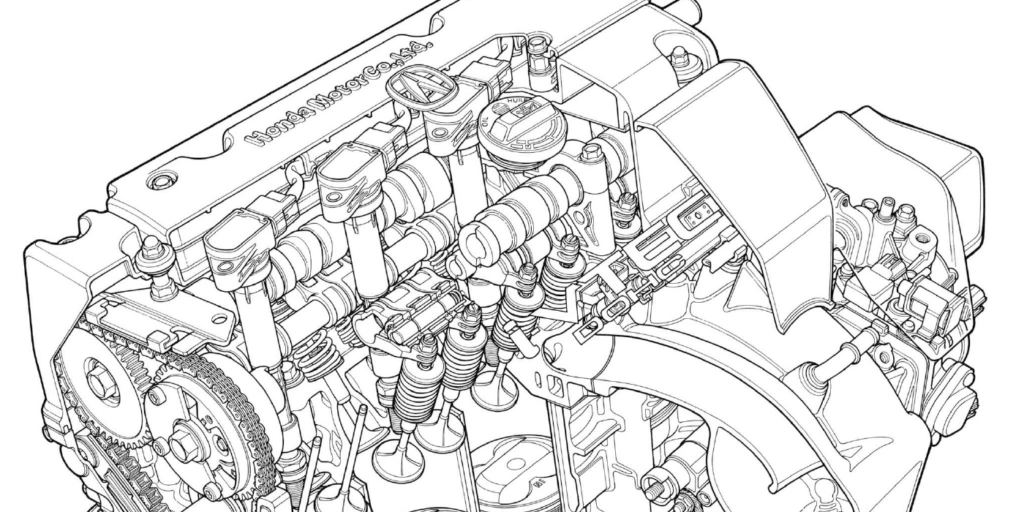
If you’ve serviced import vehicles for at least the past decade, you may have seen a Toyota vehicle that has both direct fuel injection and port fuel injection. You will see port fuel injectors in the intake manifold and a direct injection fuel pump. Toyota calls this system the D-4S or Dynamic Force Engine (the “S” stands for superior) and the earliest application was on the Lexus GS SUV with the V8. The D-4S system is not a “cold start” or “dousing” injector system, like that on V6 engines from the early to late 2000s.
The direct fuel injectors are just like any other direct fuel injection system. And, the port fuel injectors are not there to clean the intake valves; these injectors work to provide fuel to the engine. Both sets of injectors work together for the best possible fuel mixture in the cylinder.
However, port fuel injection and direct fuel injection systems each have their advantages and disadvantages.
Port fuel injection can offer better vaporization under certain conditions. But port fuel droplets can drop out of suspension when they hit the intake valve before entering the combustion chamber. Direct fuel injection is better at cooling the combustion chamber and controlling fuel trims under certain conditions. But, under certain engine speed and load conditions, direct injection can produce soot due to a lack of vaporization. Under some circumstances, port fuel injection will provide more torque.
Toyota uses its blended approach of port and direct fuel injection to give the best possible performance, emissions and economy. It is difficult to say when the port, direct or both injectors are active because it depends on many variables like throttle position, load, engine speed and even engine temperature.
D-4S Engines & Models
More and more engines are getting the D-4S injection system. It started with the Lexus on the GS models in 2007. In 2012, the Toyota/Scion FR-S F86 received the D-4S. The Highlander and Tacoma also received the D-4S systems in 2015 as an option. The latest vehicle to get it is the four-cylinder used in the 2017 Camry. The best way to spot one of these engines is to look for port fuel injectors and a high-pressure fuel pump.
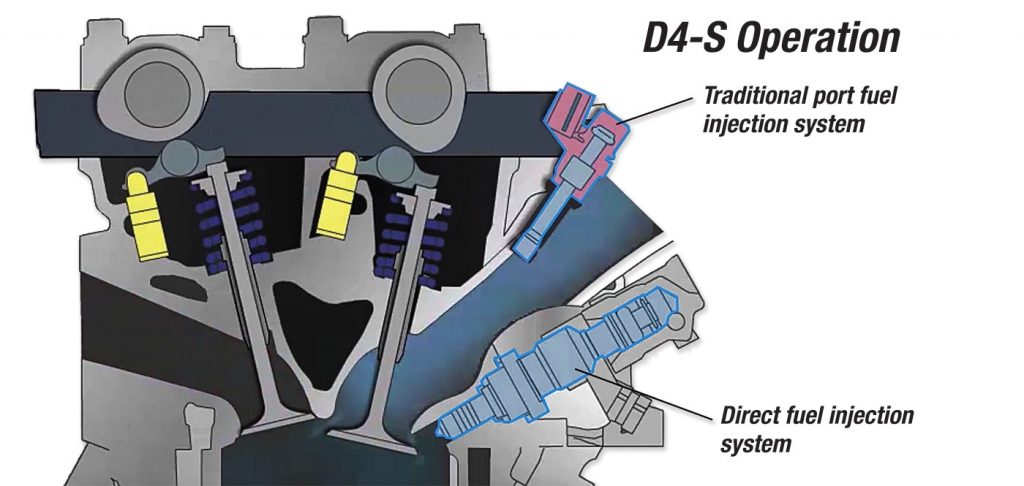
How It Works
According to Toyota, during low-to-medium engine loads, both direct-type and port-type fuel injection are used together, or one of them is used to create homogeneous mixed air and fuel, thus contributing to stable combustion processes.
During high engine load ranges, only the direct-type fuel injection is used to cool down the intake air with the chilling effect of vapors in the fuel, which is injected into the cylinder, improving charge efficiency and anti-knock properties. Under some conditions, the intake valves open to allow the homogeneous air/fuel mixture into the combustion chamber, and fuel is injected during the first half of the intake stroke.
During a cold start, the system times the opening of the port and direct fuel injector to decrease emissions and achieve stratified combustion. Immediately after a cold engine start and during the exhaust stroke, fuel is injected into the intake port from the fuel injector assembly (for port injection). Fuel is also injected from the direct fuel injector near the end of the compression stroke. This results in an air-fuel mixture that is stratified, and the area near the spark plug is richer than the rest of the air/fuel mixture. This process allows a retarded ignition timing to be used, raising the exhaust gas temperature. The increased exhaust gas temperatures promote rapid warmup of the catalysts and improve exhaust emission performance.
It is impossible to detect where the changeover from port to direct injection occurs. The only way to see the different fuel injection operations is with a scan tool.
The ECM controls the fuel pump and calculates low-pressure fuel demand based on vehicle state and the signals sent from various sensors and outputs signals. Three-phase Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control is used for the fuel pump control ECU.
Like many late-model Toyota vehicles, the fuel pump is stopped when any of the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) airbags have deployed, minimizing fuel leakage.
Both injector sets use the same fuel pump in the tank to provide fuel pressure to the fuel rail for the port fuel injectors and the high-pressure fuel pump on the engine. The pump should produce 51 to 73 psi while running and five minutes after the engine has turned off. If the pump is not working, both systems will not work.
The high-pressure fuel pump can generate 435 to 725 psi. Early D-4S Lexus V8 models with this system had a return line to the tank on the high-pressure side of the fuel system.
Later models use a spill valve and better pump solenoid control to make for a returnless system and better EVAP emissions. A spill control valve is used to control the pump discharge pressure. It is located in the inlet passage of the fuel pump assembly. The spill valve and solenoid control how much fuel is to be compressed by the high-pressure pump. It allows uncompressed fuel to spill back into the low-pressure side of the system, allowing the system to control the pressure when the direct fuel injection system is not being used. The pump will be quieter when the valve is open because it is not compressing fuel. Under some idle conditions, the usual ticking sound of the pump is eliminated.
The direct-injection fuel injectors use a special clamp that constantly pushes on the high-pressure fuel injector rail by the force of the spring. This prevents the fuel injector assembly from moving when fuel pressure is applied to the fuel injector assembly while starting the engine with low fuel pressure. The clamp reduces vibration and noise while sealing the system. These clamps should be replaced along with the recommended fittings in the high-pressure side of the fuel injection system when it is serviced.
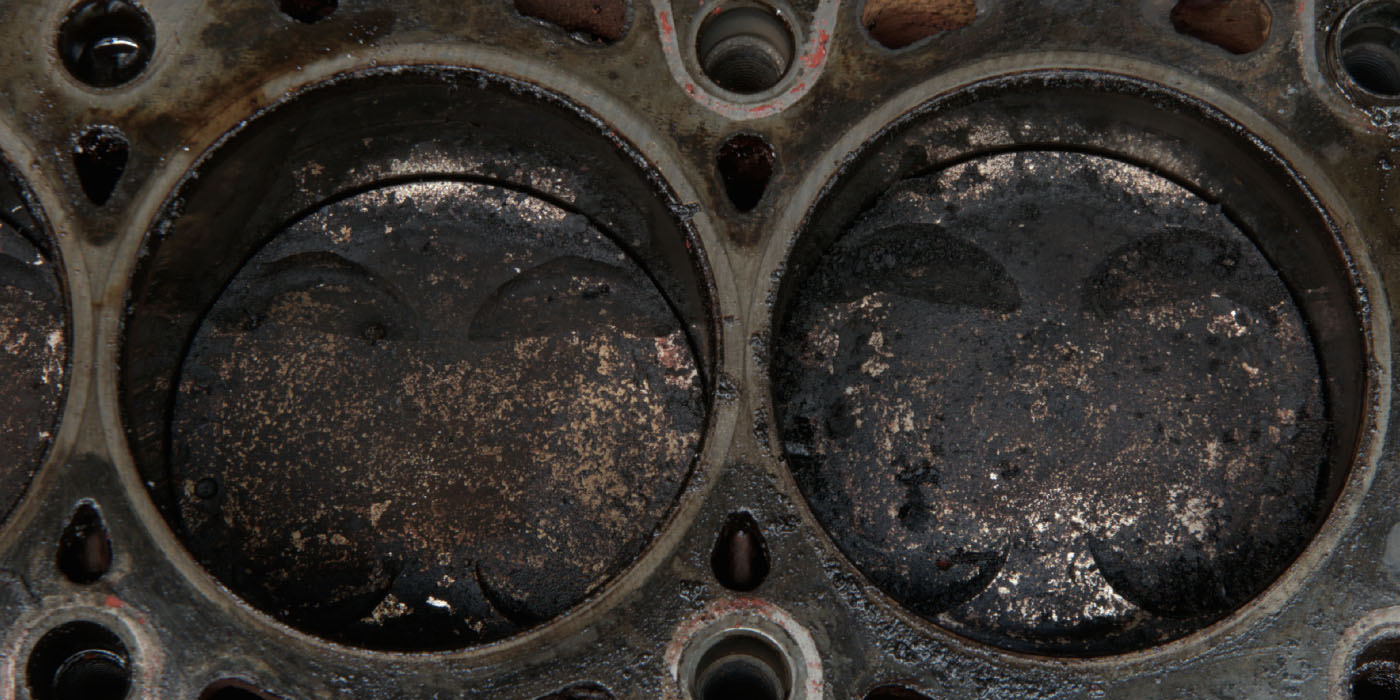
The system offers the best of both worlds while avoiding carbon buildup on the intake valves. Other manufacturers, including Audi and even Ford, are adopting the Toyota D-4S dual-injection system. As the costs of the components decrease, look for these types of systems on even more engine applications.