Condition:
Fuel System – MIL On, with DTCs P0461, P0462, P0463, B1562
Models:
Genesis Coupe 2012-’17
Sonata 2006-’17
Tucson 2010-’17
Problem:
Some customers may complain of an erratic or unresponsive fuel gauge or a fuel gauge that does not reach the full level after filling the fuel tank. Vehicles may display a check engine light on with the following DTC:
• P0461: Fuel Level Sender Circuit Range/Performance
• P0462: Fuel Level Sender Circuit Low Input
• P0463: Fuel Level Sender Circuit High Input
• B1562: Fuel Sender ERR (YF Only)
Inspection Procedures:
Note: The vehicle should be parked on a level surface before checking the fuel level.
1. Turn the engine off and wait at least 40 seconds.
2. Gain access to the fuel pump.
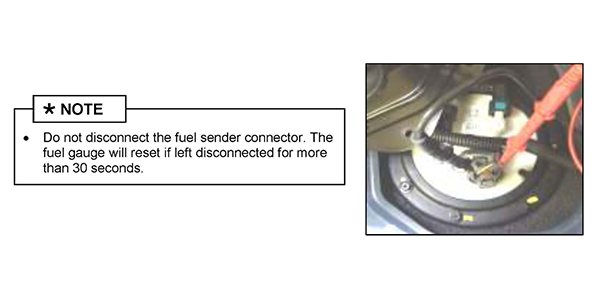
3. Locate the fuel sender connector (A) on top of the fuel pump.
4. Set your multimeter to ohms and back-probe the fuel sender connector (A) to measure the resistance between pins 1 and 3.
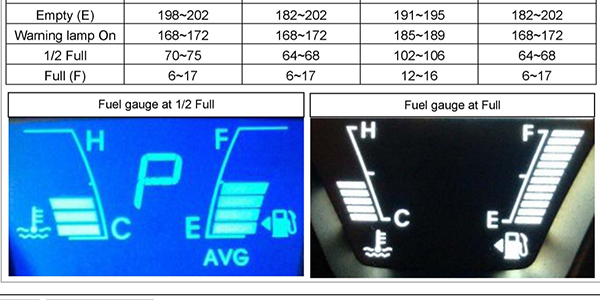
5. Compare the measured resistance and the fuel gauge reading with the specifications.
6. If the resistance is out of specification, or there is an open circuit, go to the sender sweep test.
Sender Sweep Test:
1. Disconnect the fuel sender connector and remove the fuel pump and fuel sender assembly.
2. Measure the resistance between pins 1 and 3 on the fuel sender connector terminal.
3. Record the resistance at several positions of the fuel sender float arm (B).
• Lift the float arm to its highest position to take a “Full” reading.
• To take an “Empty” reading, let the float arm rest at its lowest point.
4. Compare resistance measurements with the specifications shown in the Resistance Specifications table above. If the measured resistance is within specifications, go to the related wiring inspection.