Applicable model(s)/VINs:
2007-’11 CX-7 2.3L Turbo vehicles with VINs lower than JM3ER******352482 (prod. before Sept. 29, 2010)
2007-’11 Mazdaspeed3 vehicles with VINs lower than JM1BL******398222 (prod. before Sept. 29, 2010)
2006-’07 Mazdaspeed6
With the engine warmed up, some vehicles may exhibit a knocking/rattle type noise from the front timing cover and/or valve (cylinder head) cover below 2,000 rpm.
The noise is caused by excessive stretching of the timing chain.
Repair Procedure:
1. Verify that proper oil change intervals have been performed.
2. Verify that the noise is coming from the front timing chain cover and/or cylinder head area.
Service Tips:
– The noise is heard inside the vehicle with all of the windows rolled up, all accessories turned off and engine running at normal operating temperature.
– The knock pulse is at camshaft speed (1/2 the engine rpms).
– The knock can usually be felt on the No. 3 engine mount.
3. Remove the engine front cover according to the on-line MS3 instructions or the workshop manual.
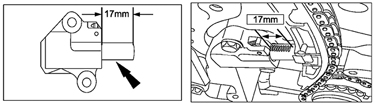
4. Check the protrusion length of the chain adjuster plunger.
– If it’s 17 mm (nine exposed notches) (see Fig. 1) or more, replace the timing chain with a modified one according to the on-line MS3 instructions or the workshop manual.
Note: Do not replace the chain adjuster.
– If it’s less than 17 mm, the noise is not the result of the timing chain stretching concern. Refer to the “Engine Noise” diagnostic procedure in TSB 01-036/10 “Diagnostic Procedure For Engine Noise Repair.”
5. Verify the repair.
Courtesy of ALLDATA.