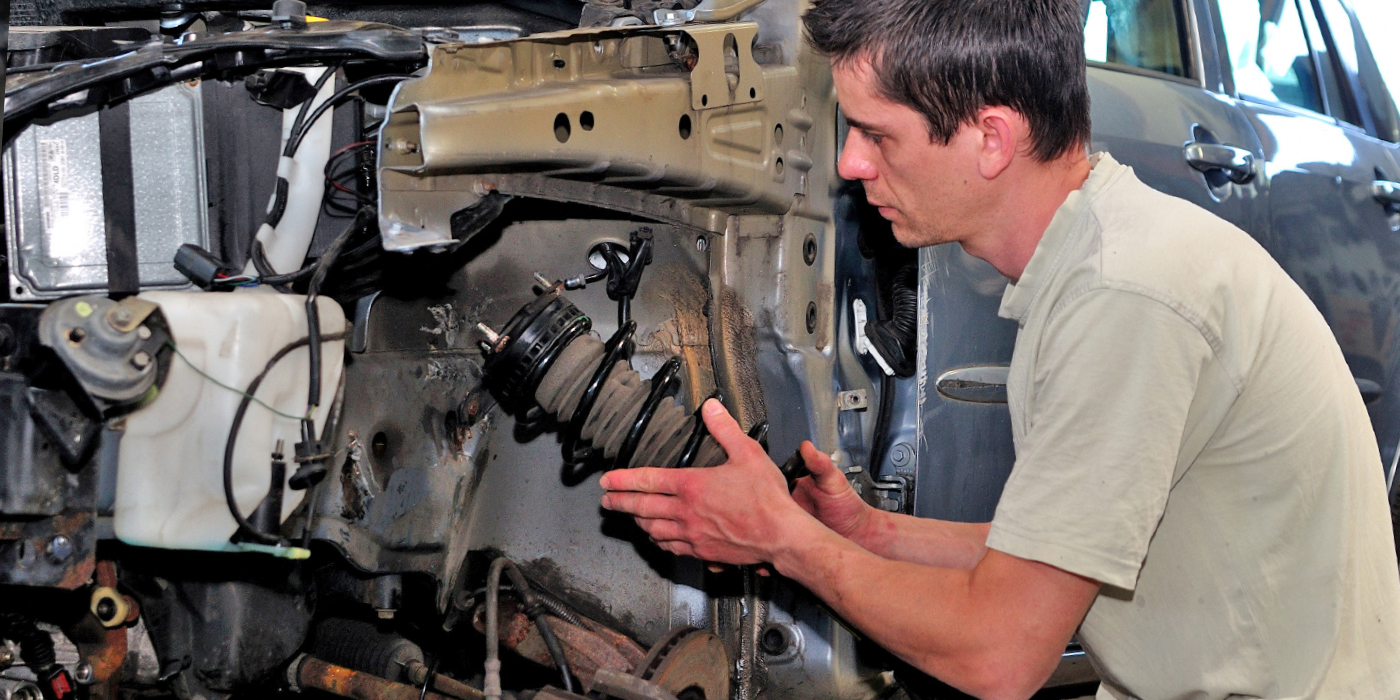
Manual gearboxes are relatively trouble-free and long-lived, provided they are not abused too severely. The clutch, however, is a wear component. With every shift the clutch must be disengaged and engaged. Stop-and-go driving in heavy traffic is especially hard on a clutch because the driver is always riding the clutch pedal. After millions of such cycles, the clutch eventually wears out. It may start to slip, chatter or make noise.
Parts that wear out and may have to be replaced include the pressure plate, friction disc, release bearing, pilot bearing or bushing (if used) and components in the clutch linkage (the cable, cable adjuster, or in a hydraulic linkage the master or slave cylinder).
Most clutches have a diaphragm spring but some older vehicles have coil spring clutches with nine to 12 coil springs. Diaphragm clutches are used on most newer vehicles because they require less pedal pressure to release than coil-spring clutches, are less complicated, last longer and actually increase the clamp load on the clutch disc as it wears (up to a point).
The clutch disc has friction linings on both sides that grab the flywheel and pressure plate. Engaging the clutch creates friction, which generates heat. Consequently, the clutch linings can get very hot. The flywheel and pressure plate both act as heat sinks to help carry heat away from the clutch and cool it. If the clutch gets too hot from excessive slippage or loading, the linings may burn, damaging the clutch.
The release bearing that pushes against the diaphragm spring in the clutch or the release fingers on a coil spring-style clutch has ball bearings to reduce friction. If the release bearing wears out, it can make noise when the clutch pedal is depressed. It can also damage the clutch spring or release fingers if it binds up. On most clutches, the release bearing is held in a yoke or fork that pivots on a ball stud when the clutch linkage moves. On some vehicles, a telescoping hydraulic release bearing is used inside the bellhousing to operate the clutch. Wear or damage to any of these components can also affect the operation of the clutch.
Older vehicles mostly use a mechanical linkage or a cable connected to the clutch pedal to operate the clutch. Most newer vehicles have a hydraulic clutch linkage. With both types of linkages there are usually return springs and some type of linkage adjustment for the clutch. Accurate adjustment is essential for proper pedal travel and clutch operation.
The labor required to replace a clutch can be four to six hours or more so most experts recommend replacing all of the major clutch system components at the same time. Installing a complete clutch kit includes the clutch pressure plate, disc, release bearing and pilot bearing or bushing. Clutch kits also eliminate the risk of mismatched parts, which can sometimes happen when different clutch components are sourced from different suppliers.
Another item that needs attention when the clutch is replaced is the flywheel. The surface of the flywheel must be clean, smooth and flat. After years of use, it is often scored, grooved and out-of-flat. If runout exceeds specifications and/or the surface is worn, the flywheel must be resurfaced. Some clutch suppliers will not honor a clutch warranty if the flywheel was not resurfaced when the clutch was installed.
Some engines have a “dual-mass” flywheel which is like two flywheels in one. A dual-mass flywheel helps dampen engine vibrations and cushions clutch engagement for smoother operation. If a dual-mass flywheel is cracked, damaged or the internal springs have failed, it must be replaced. Resurfacing dual-mass flywheels is not recommended. If the flywheel is warped, deeply grooved or worn excessively, it should be replaced. Dual-mass flywheels are very expensive. They can be replaced with a conventional one-piece solid flywheel, but this will require a different clutch set than the original dual mass flywheel.