Service and replacement is making a comeback
on some vehicles
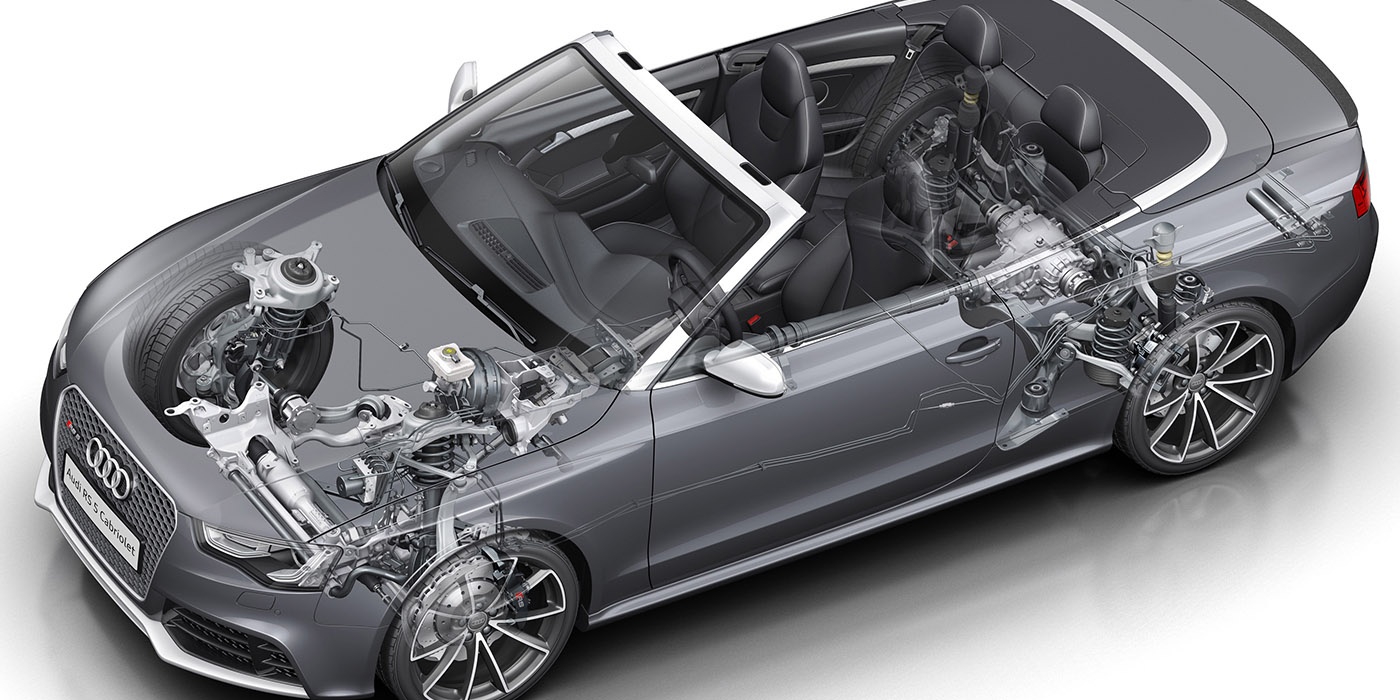
Some people think servicing wheel bearings is a thing of the past — like measuring dwell on a set of ignition points. But, even with sealed hub units, inspection and service have not gone out of style. Like any moving part on a vehicle that is subject to wear and contamination, wheel bearings can and do wear out.
The average life of a sealed wheel bearing and hub assembly is about 85,000 to 100,000 miles. Consequently, you may only have one chance during a vehicle’s life to replace these parts. Miss that opportunity and it may be gone forever.
Recently, we have seen some domestic manufacturers reverting back to serviceable wheel bearing designs that use a captured rotor like in the case of the GM mid-sized trucks.
 Diagnostics
Diagnostics
The first symptom of wheel bearing trouble is usually noise. A rumbling, growling, chirping or cyclic noise of any kind from the vicinity of the wheels is a good indication that the bearings need to be inspected without delay.
Wheel bearing noise is usually proportional to vehicle speed, and does not change when accelerating, coasting or decelerating (which distinguishes it from differential, transmission or U-joint noise). The noise may change when turning, or become louder or even disappear at certain speeds. But it shouldn’t be confused with the clicks and pops produced by a worn or damaged outer CV joint on a FWD car. A bad outer CV joint usually only makes noise when turning, not when driving straight ahead.
If a sealed bearing assembly is noisy or feels rough when the wheel is spun by hand, it needs to be replaced. If the bearings are the serviceable kind, they need to be removed, disassembled, cleaned and inspected. If the rollers, balls or races are worn, pitted, cracked or show any damage, replacement is required.
A bearing failure can be dangerous because it may cause the wheel to separate from the vehicle and/or cause a loss of steering control! It’s not something to ignore or put off because there’s no way to know how many miles the bearings will go before the unit fails completely.
The other safety issue involved is the ABS system. As long as the ABS warning light remains on, the ABS system is disabled. This should not affect normal braking, but it will prevent the ABS system from helping out in an emergency or when braking on a slick surface.
Replacing a sealed wheel bearing and hub assembly involves removing the wheel, hub nut and brakes to replace the unit. Do not use an impact wrench for removal or installation. Use a torque wrench and tighten all bolts and nuts to specifications.
Many hub units for FWD applications come with a new hub nut. Use it. And, be sure to torque it to specifications with a torque wrench. Never use an impact wrench.
Another problem that may occur with older, serviceable wheel bearings is incorrect adjustment. Too much play can allow steering wander (which may be mistaken for worn steering components or the need for an alignment). One way to check wheel-bearing play is to raise the wheels off the ground and rock the tires in and out while watching for any looseness. As a rule, there should be no play on most FWD cars, but up to .010 inch of play in the front bearings may be acceptable on RWD cars and trucks with adjustable bearings.
If there’s play in sealed bearings, replacement is necessary. But if the bearings are the adjustable variety, a simple adjustment might be all that’s needed.
In any event, loose wheel bearings should not be adjusted until the bearings have been removed and inspected for possible damage. Bearings do not loosen up under normal use. So if the bearings feel loose, they may be adjusted too loose, worn or the hub nut may have backed off (a broken cotter pin or retainer).
Serviceable Bearings
Wheel bearings that are not factory sealed, like on the 2WD Ford F-Series and GM Colorado and Canyon models, are starting to make a comeback. In the future, many will be neglected and never receive any maintenance whatsoever except maybe when someone is doing a brake job. Serviceable bearings should be cleaned, inspected and repacked with fresh, clean wheel bearing grease every 30,000 miles or according to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations.
When wheel bearings are serviced, the old grease should first be removed and the bearings cleaned and inspected before being repacked with fresh grease. This will remove any contaminants from the hub that may cause problems later on, and eliminate any risk of incompatibility between the old and new grease.
Use a quality high temperature wheel bearing grease (a #2 NLGI lithium-based grease, for example) or a synthetic wheel bearing grease. Three heaping tablespoonfuls is usually enough for most car and light truck hubs. The hub should not be packed solid with grease to allow room for expansion. When wheel bearings are installed, use new grease seals. Never reuse old seals. Used seals can leak and contaminate brake linings or cause premature bearing failure.
Adjust the bearings to specifications. Overtightening adjustable tapered roller bearings is a common error that can lead to premature failure. Tapered roller bearings on the front of RWD vehicles are never preloaded. They’re snugged up with no more than 15 to 20 ft. lbs. of torque while rotating the wheel to make sure the bearings are seated. Then the adjustment nut is loosened 1/6 to 1/4 turn, and locked in place with a new cotter pin. As a rule, end play should be about .001 to .005 inches.
On FWD cars with adjustable tapered roller rear wheel bearings, the bearing adjustment procedure is usually the same as with RWD vehicles (zero preload), but some do require a slight preload. If one wheel bearing has failed, pay close attention to all of the other hubs on the vehicle, too, especially if the vehicle has a lot of miles on it. Chances are some of the other bearings may also be nearing the end of their journey.
When a customer hears how much it’s going to cost to replace the hub assembly, he may suffer an instant attack of sticker shock. But he doesn’t really have any other options. As we said earlier, the bearing assembly is a sealed unit and can’t be repaired or rebuilt. The part is expensive and requires a lot of labor to install. If he ignores the warning signs and does not have the hub replaced, it will only get worse.