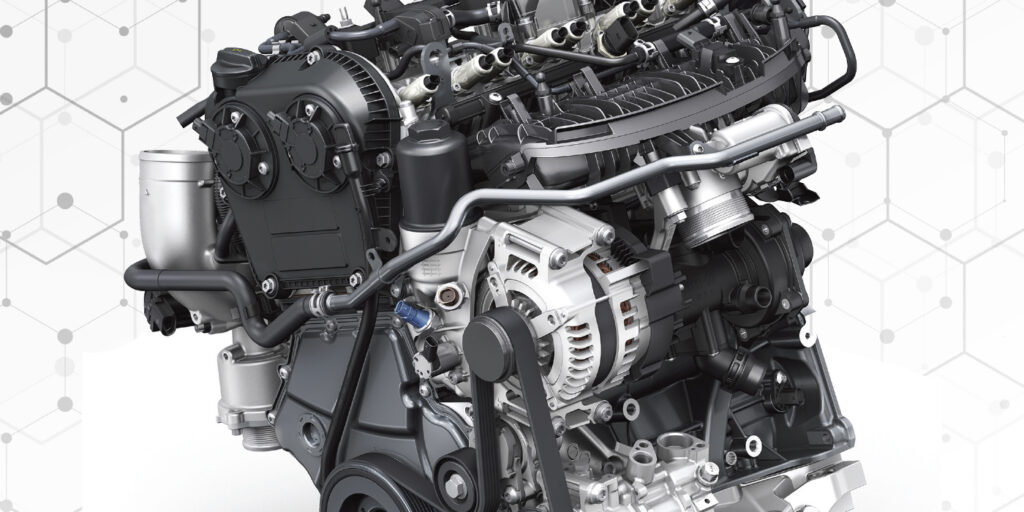
The Audi and VW 2.0L TFSI, TSI and FSI engines have been around for almost 15 years. In that time, Audi/VW have made endless revisions and updates to the hardware and software. The one thing they can’t change, however, is the customers who fail to perform regular maintenance. This is often the case with the 2.0L engine and the occurrence of carbon deposits.
Technical Service Bulletins can be valuable in helping solve vehicle problems. But sometimes it takes multiple TSBs to find a pattern failure or the “root cause” of a problem. In the case of the Audi/VW 2.0L Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) engine introduced in 2006, three problems related to engine carbon and fuel issues are connected through multiple TSBs.
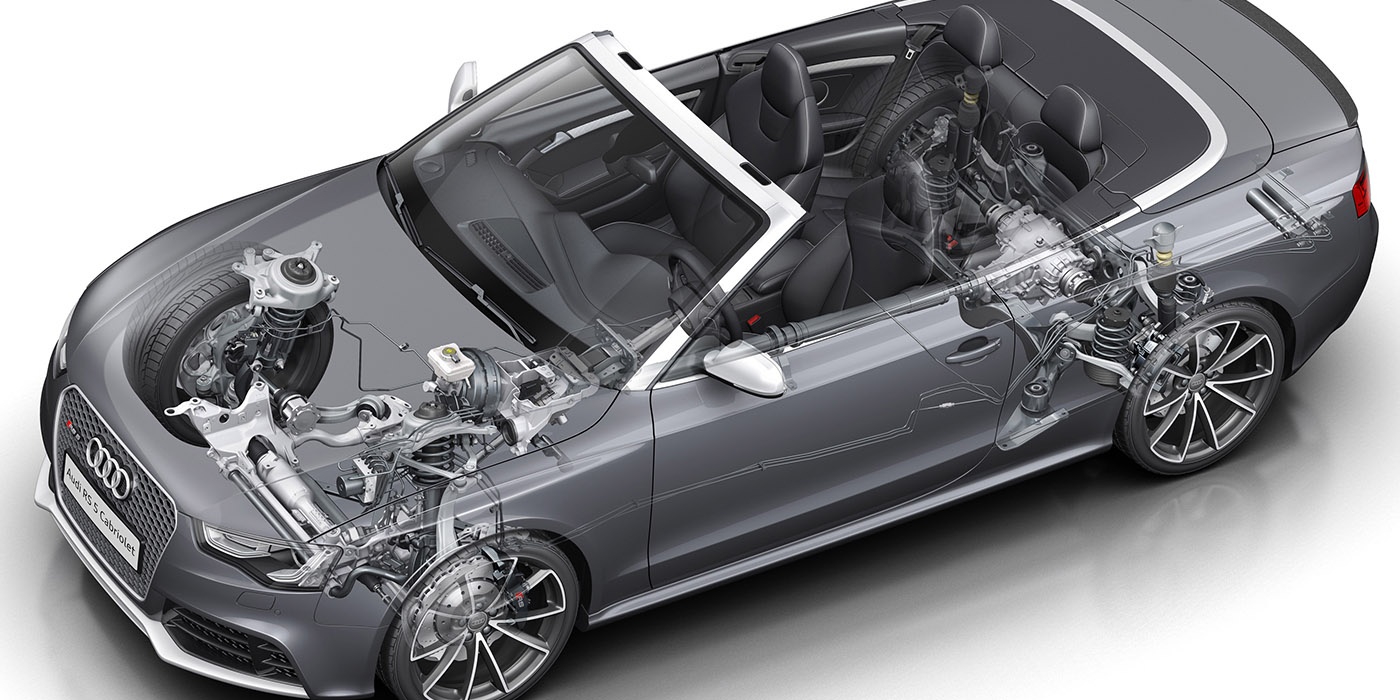
The 2.0L FSI engine was one of the first gasoline direct injection engines from Audi. When it was introduced in 2006, the turbocharged engine had a lot of improvements over the 1.8T engine, as well as many new components. The problem engines can be found in 2005-‘07 A3 and A4 models with the engine codes BPG, BPY or BWT.
Carbon and fuel problems with the 2.0L FSI engine have multiple causes, symptoms and solutions. While there is not a single TSB from Audi that clearly outlines the problem, you can connect the dots to realize the problems with oil consumption that damage the top end of the engine and cause carbon buildup.
OIL CONSUMPTION
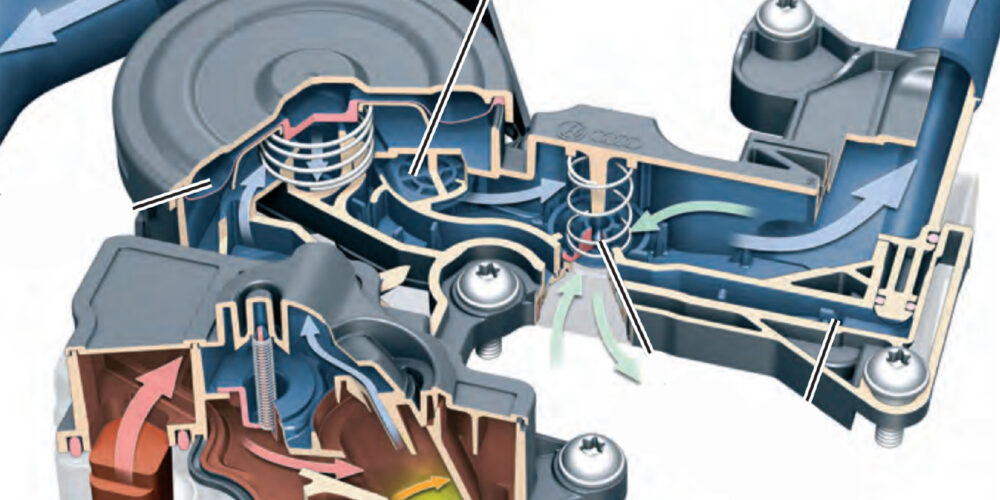
TSB 2015505/1 discusses increased oil consumption and blue smoke. Upon inspection, oil can be found in the air intake hoses after the turbocharger and the oil can be seen leaking from the oil filler cap.
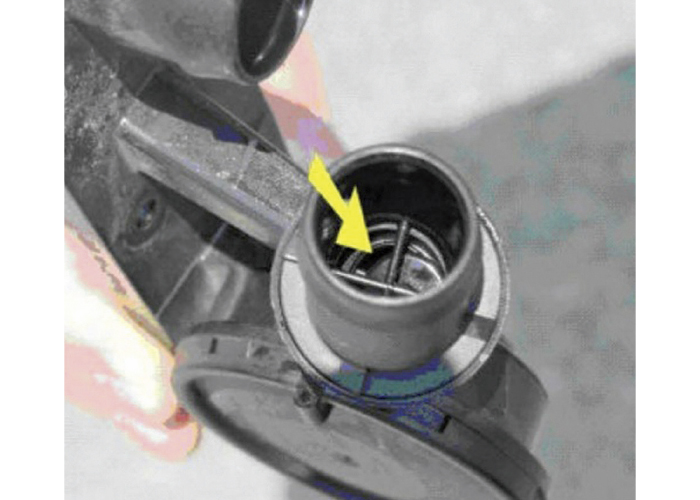
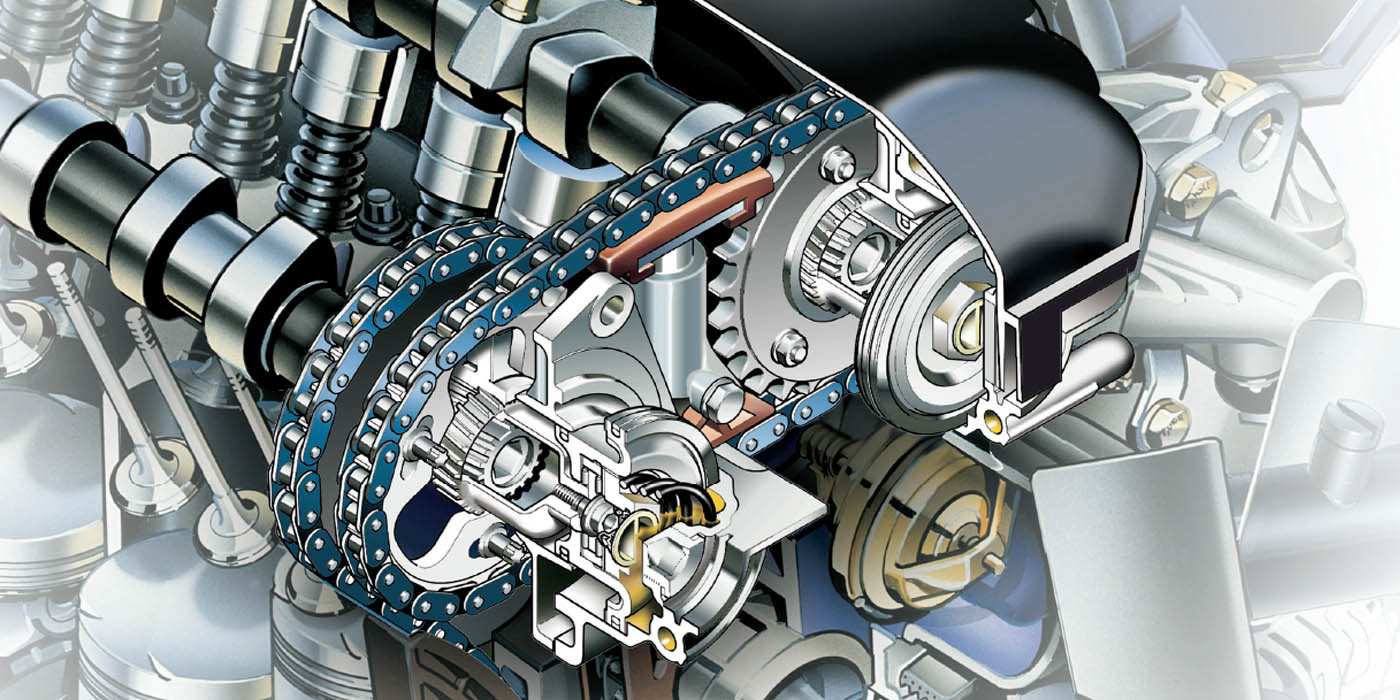
The cause of the problem is that the guide pin that is part of the check valve in the intake manifold side of the valve may break, preventing the check valve from correctly sealing when boost pressure is present in the intake manifold. Intake boost pressure will be applied to the engine crankcase, resulting in oil leaks and the prevention of engine oil from properly draining from the turbocharger through the oil return line.
Even though the TSB does not mention wear to the camshaft or carbon buildup, we all know what happens when the oil gets low or the PCV is not functioning properly.
OIL TSB
TSB 2010046/4 was issued in 2008 and it advises the use of VW/Audi 502 00 specification engine oil or the aftermarket equivalent (ACEA A3, ACEA A5 or ACEA B5, API SL or ILSAC GF-3). The TSB recommends that the owner always carry a spare quart of oil that meets the standards in case the engine oil level needs topping off while on the road. This TSB was superseded by 2010043/14 issued in March 2015. The only update was a complete list of approved oil brands.
This TSB is a warning that substandard oils could cause damage to the engine and catalyst due to the oil consumption problem discussed in TSB 2015505/1, which advises replacement of the PCV check valve. It is also a warning that low-quality oils could cause damage to the high-pressure fuel pump lobes on the camshaft and the plunger on the pump.
CAMSHAFT AND HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL PUMP PROBLEMS
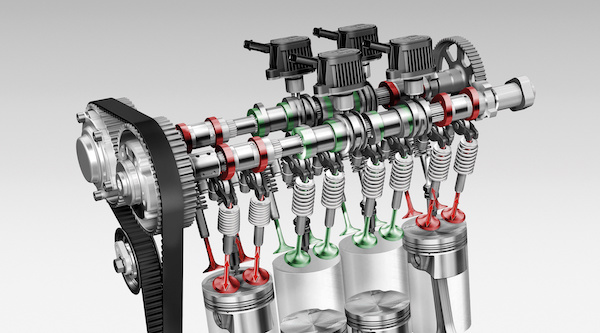
TSB 2013147/13 is probably the most infamous Audi TSB on the FSI engine. It outlines the conditions that cause DTCs P2293 (Fuel pressure regulator 2 performance), P0087 (Rail fuel pressure too low) and P1093 (Fuel trim 2, bank 1 malfunction). The source of these codes is excessive wear on the camshaft lobes on which the high-pressure fuel pump rides.
Excessive wear of the cam lobe limits the maximum pump piston lift, causing fuel rail pressure fluctuations. The wear on the cam lobe also leads to wear in the base of the high-pressure fuel pump plunger, and this is the cause of the codes for the fuel pressure and fuel trim.
The solution in the TSB is to replace the camshaft with one that has “increased surface hardening” and replace the plunger/follower if it is damaged. But you have to ask yourself whether one of the largest automakers would put an engine on the market with a camshaft that wears out. The theory is that the level and quality of the oil leads to the failure of the pump. The level of the oil is connected to the oil consumption problem discussed in TSB 2015505/1.
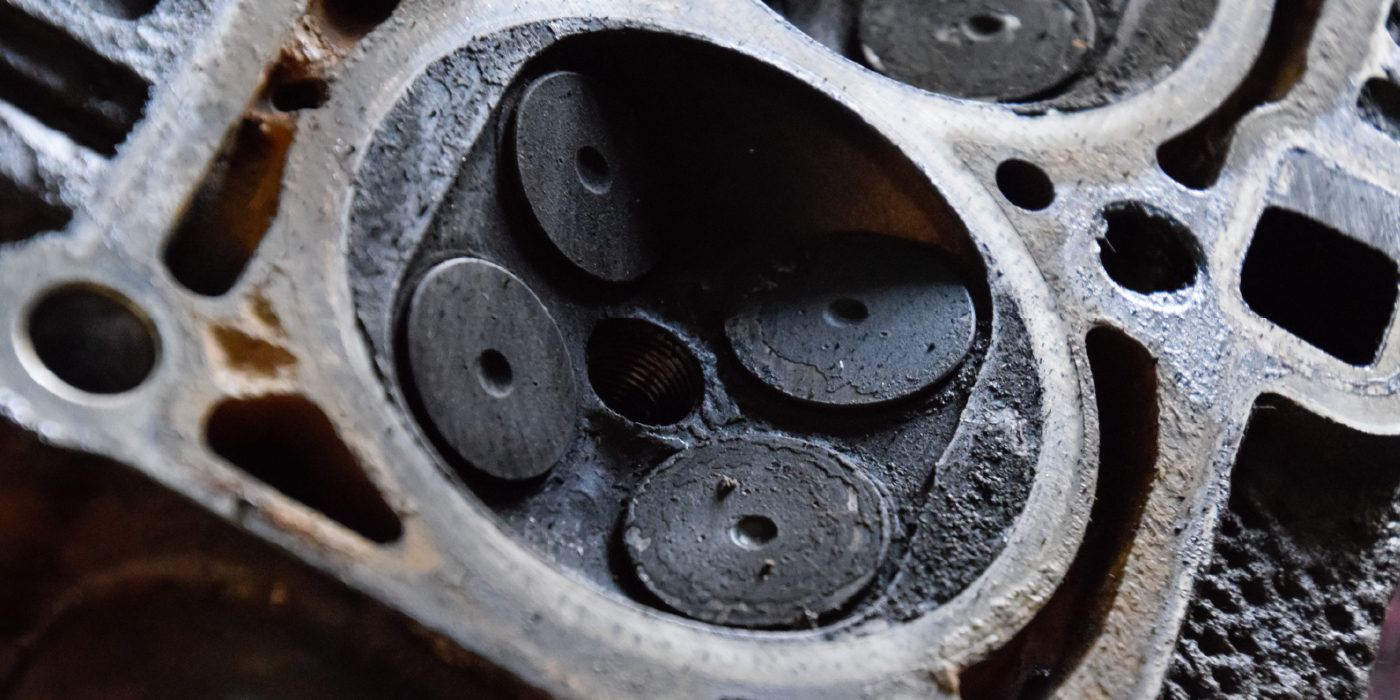
You do not have to be Sherlock Holmes to connect the dots on the related problems with the 2.0L FSI engine. The oil requirement and oil level TSBs were written because of the PCV problem causing issues with low oil levels between oil changes. The low oil level compounded by the addition of low-quality oils causes damage to the lobes on the camshaft that power the high-pressure fuel pump. This also causes carbon deposits on the intake valves and piston and cold-start misfires.
So what is the moral of the story? Across multiple TSBs, the root cause is oil and crankcase vapors that induce direct injection problems and carbon buildup. What can make the problem worse? Customers who neglect regular oil changes or use low-quality oils.