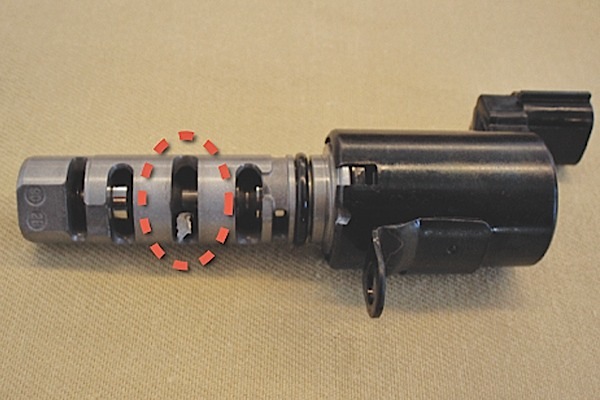
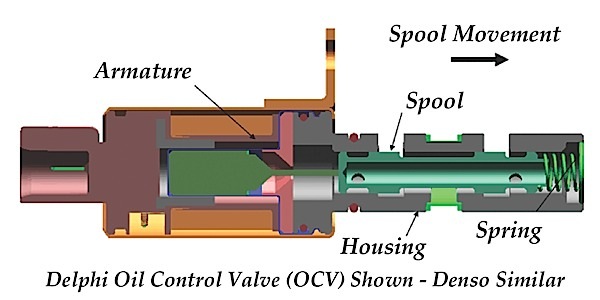
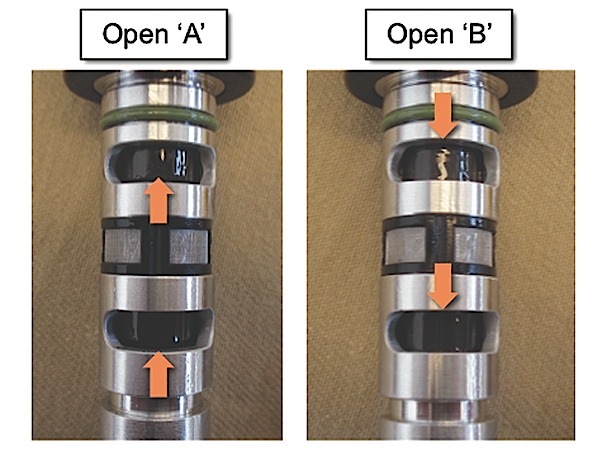




Nissan’s steering system is susceptible to driver-error.
Nissan’s electro-hydraulic power steering system provides the same feel of a conventional hydraulic power steering system while improving fuel economy by using an electric motor to power the pump. The system is comprised of the electro-hydraulic pump assembly, control module and steering gear.
The power steering module is on top of the pump, and the motor controls the speed of the power steering pump according to vehicle speed and steering angle. By changing the pump speed, the module controls the steering assist force. The control module is connected to the hi-speed CAN bus that ties the engine control module (ECM) and ABS module. The ABS module provides vehicle speed and steering angle, and torque data to the power steering system. The connection to the ECM allows the alternator to provide enough power when the pump is running.
The brake system of a hybrid may have multiple components to perform regenerative braking and pedal simulation.

Regenerative braking takes the forward motion of the vehicle and turns it into electrical energy.
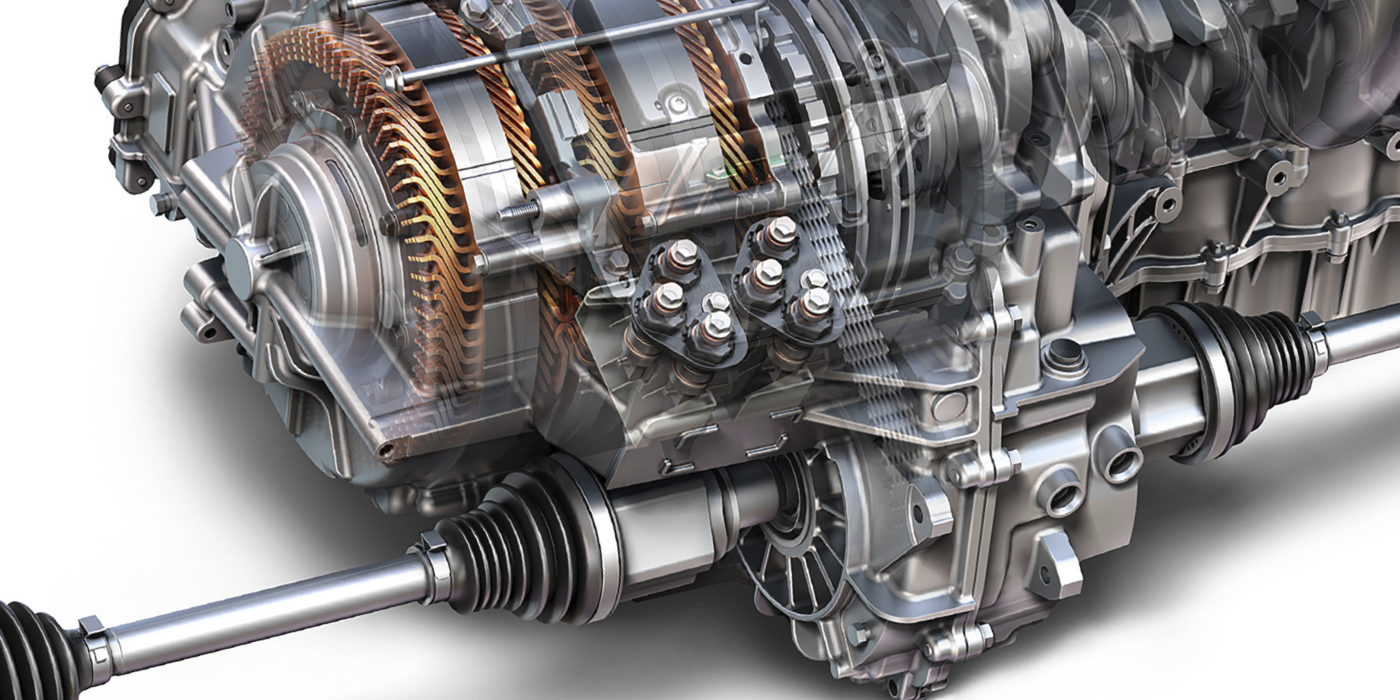
A second generation Toyota Prius is at least 12 years old and batteries may need to be replaced. Here’s what the codes mean.

The secret to diagnosing air ride problems is knowing what criteria the system uses to regulate the compressor/reservoir and having the right tool.

The April issue includes technical and management content and is free to download.

It uses a 3-layer filter to deliver cleaner, healthier, fresher air on the go, Lumileds said.
The campaign aims to raise $65,000 through 1,000 donations of $65 each.
The release provides new coverage in 53 distinct product categories and 47 part numbers for 2023 and 2024 model-year vehicles.