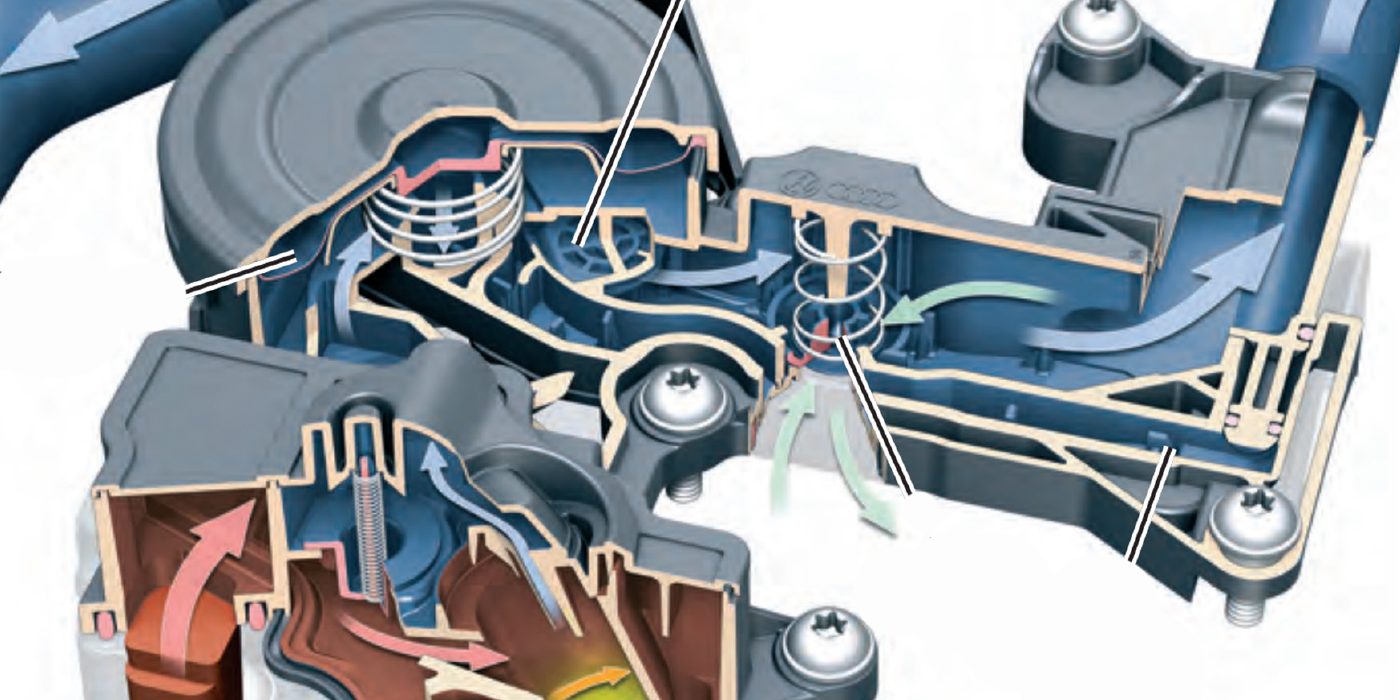
Anyone who services vehicles like yourself knows that the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve prevents crankcase blowby vapors from escaping into the atmosphere by siphoning the vapors back into the intake manifold so they can be reburned in the engine.
Anyone who services vehicles like yourself knows that the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve prevents crankcase blowby vapors from escaping into the atmosphere by siphoning the vapors back into the intake manifold so they can be reburned in the engine.
They’ve been around since 1968 on most vehicles, and the main component is a spring-loaded PCV valve that meters airflow.
Mounted in the valve cover and connected to the intake manifold, carburetor or throttle body with a large vacuum hose, the PCV valve plays an important role in vehicle performance.
Did You Know…
If the engine has an external air leak you will not have an effective PCV system. This could be a leaking front cover, rocker cover, oil pan gasket, manifold end gaskets or any other host of potential leaks.
PCV Use
Intake vacuum pulls fresh air into the crankcase through a second breather hose. As the air passes through the engine, it picks up blowby vapors and moisture before it is pulled through the PCV valve and back into the engine. The PCV valve changes the flow rate according to engine load and throttle position.
PCV helps extend oil life by removing moisture that causes sludge. If the PCV valve or hose becomes clogged, moisture can rapidly accumulate in the crankcase causing engine-damaging sludge to form.
A plugged PCV may also allow pressure to build inside the engine causing oil leaks.
A quick check of the PCV valve is to shake it and listen for a rattle (no rattle would indicate a blockage). Another is to pull the valve from the valve cover and feel the end for vacuum while the engine is idling (no vacuum would indicate a blockage). The recommended replacement interval is typically 50,000 miles.
Some engines do not use a PCV valve for crankcase ventilation, but have a breather box that serves the same purpose.
On some older vehicles, a small PCV air filter is mounted inside the air cleaner. This filter should always be inspected and cleaned or replaced as needed on a regular basis.
Most emission control parts, like the PCV valve, require little if any scheduled maintenance, but replacement may be necessary if the Check Engine light is on, the vehicle has failed an emissions test or is experiencing a driveability problem.
Other emission control components include the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve, the evaporative emission control system (EVAP) vapor canister and purge valves, the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors and all of the engine’s other engine management sensors.
The PCV valve should be inspected and cleaned every 50,000 miles, or replaced as needed (if clogged or malfunctioning).
Did You Know…
All PCV valves are not created equal. They have different flow characteristics that are specific to each engine application and may even be specific to particular platforms using the same engine.
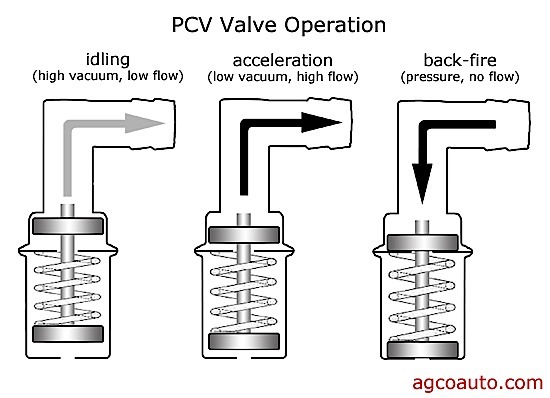
Testing a PVC Valve
Testing the PCV system is relatively easy and can be done a number of different ways:
• Pinching: After running the engine up to operating temperature and allowing it to stabilize at idle, pinch or block off the hose between the vacuum source and the PCV valve.
The engine should typically drop 50-80 rpm. If the engine does not change, check the PCV valve and system hoses for blockage.
Replace components as necessary and retest.
• Vacuum with gauge: Run the engine up to operating temperature. Shut the engine off and block off the fresh air source to the engine.
This would typically be the hose coming from the air cleaner to the rocker cover.
Remove the dipstick tube and connect a vacuum-pressure gauge to the dipstick tube. Restart the engine and allow it to stabilize at idle. Then take a reading of your vacuum-pressure gauge.
You should read 1-3” of vacuum with a normally operating PCV. If you have 0” of vacuum or even pressure, you have problems.
• Vacuum without a gauge: Another way to perform a vacuum test on a PCV valve is to start the engine and bring it to normal operating temperature.
Next, disconnect the hose from the remote air cleaner or air outlet tube.
Place a stiff piece of paper over the nipple or hose end and wait 1 minute. If vacuum holds the paper in place, the system is okay; reconnect the hose.
If the paper is not held in place, the system is plugged or the evaporative emission valve (if equipped) is leaking.
Inspect the PCV valve and grommet for deterioration, and replace if necessary.
If Left Unattended….
A neglected or poorly operating PCV system will quickly contaminate the engine oil and heavy sludge accumulations will begin to form.
Imagine dumping water and acid into your engine oil on a daily basis: how do you think that would impact the bearings, pistons and oil characteristics?
For that matter, how long do you think the engine would last by doing that? That is exactly what an improperly functioning PCV system will do because that is what the combustion process blowby contains.