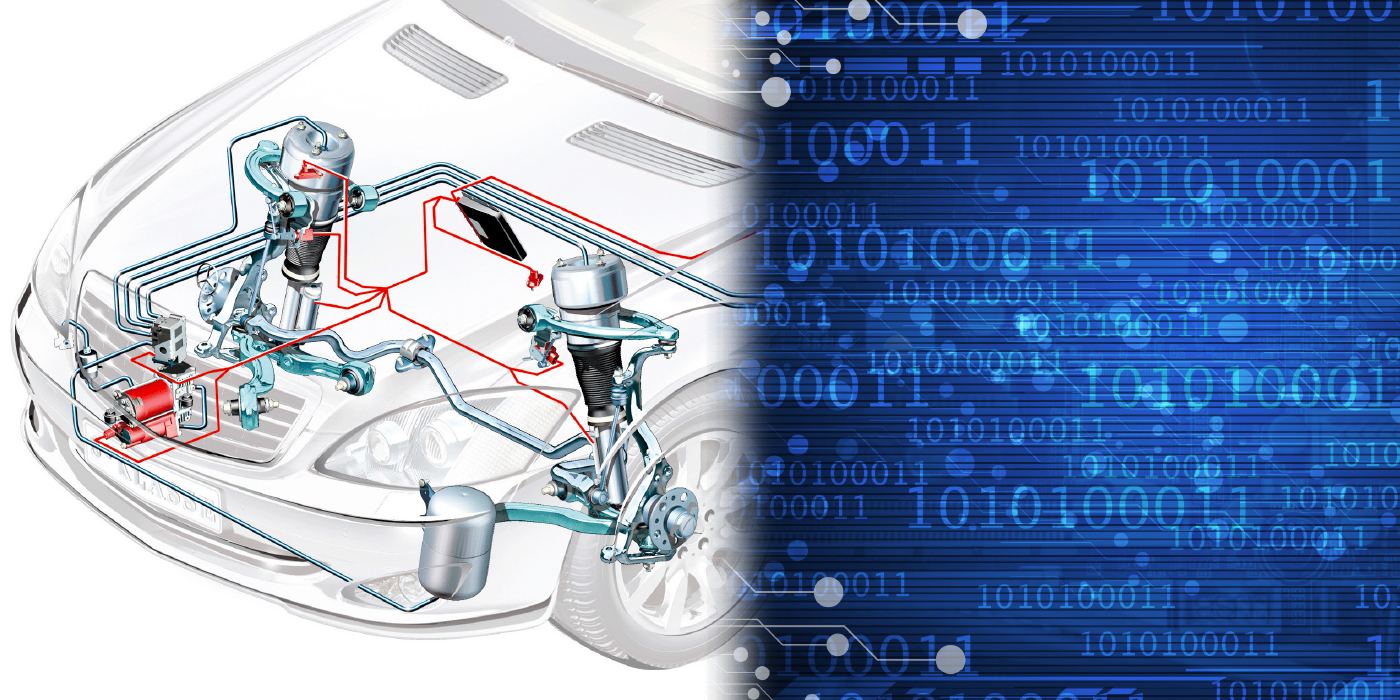
When rims have larger diameters, the wheel assembly weighs more because rubber and air have been replaced with metal. In the past 20 years, the rim diameter of the Toyota Camry V6 has gone from 15-inches to 18-inches. This extra weight means that the springs and bushings have to control more mass. This mass is not constant. As the wheel assembly hits bumps, it accelerates upwards with greater force. If the bushing or spring can’t control this movement and force, the suspension becomes fully compressed and damage can occur. It is also why the control arms and bushings have changed on the Toyota Camry.
Most modern bushings augment the geometry of the suspension. As the vehicle loads the suspension, movement in the bushings can change the toe, camber and caster so that the vehicle is more stable under braking, cornering and acceleration. This is all done without sacrificing tread life or fuel economy while traveling in a straight line.
Modern suspension bushings act like a progressive spring. As the bushing is loaded in different directions, the first few millimeters of movement might occur with very little effort. As the load increases, the bushing will become stiffer. Also, a control arm bushing may react different to loads caused by braking and those caused by side loads.
To have these progressive qualities, the structure of the bushing can be complex. You may see different structures, voids and materials in a bushing. Some of these voids may pass all the way through the bushing.
Some bushings may have chambers filled with fluid. These are commonly called hydraulic bushings. As loads are put on, the suspension fluid will pass between the chambers. Since a fluid is not compressible like the soft components, movement of the suspension can be controlled in a more predictable manner. Also, the oil and chambers help to isolate the vibration and noise from the tires. When hydraulic bushings fail, they will leak.
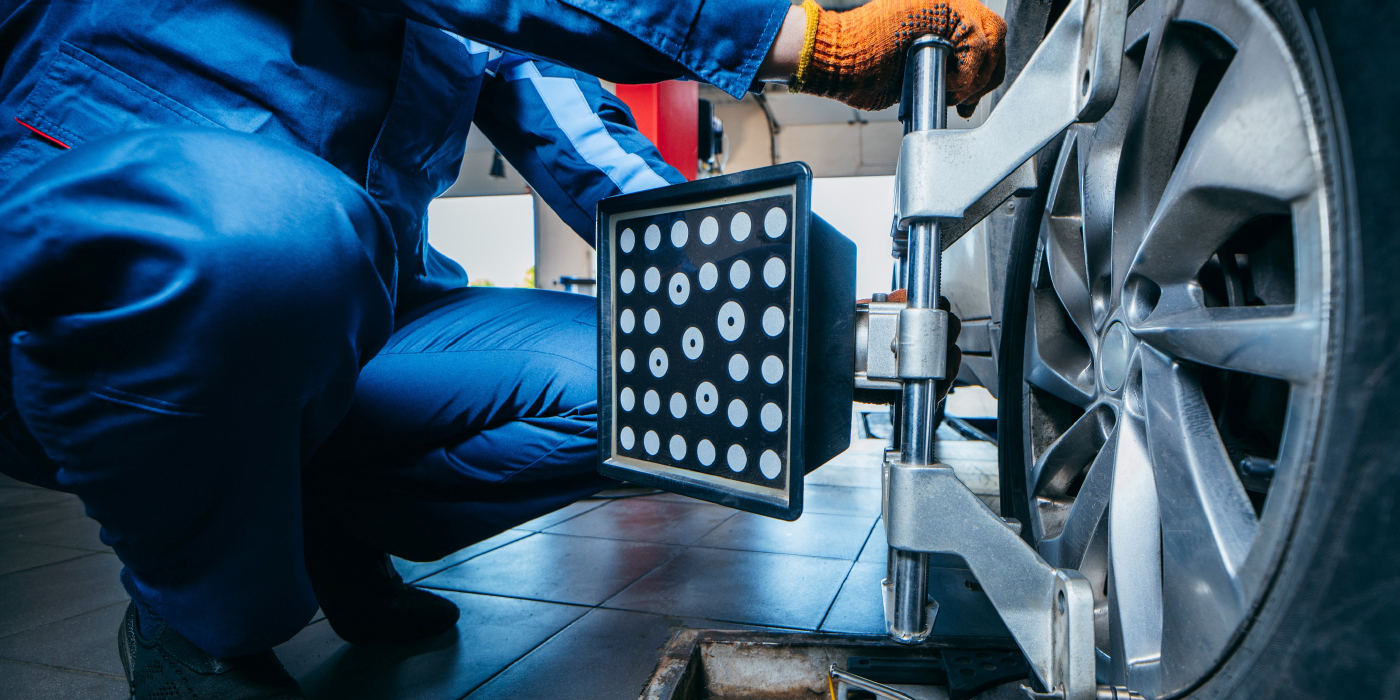
With these advanced bushings, the alignment of the bushing is critical. A difference as little as 7 degrees in how the bushing is installed can change how the bushing operates. This can eventually lead to the premature failure of the bushing.
Inspection
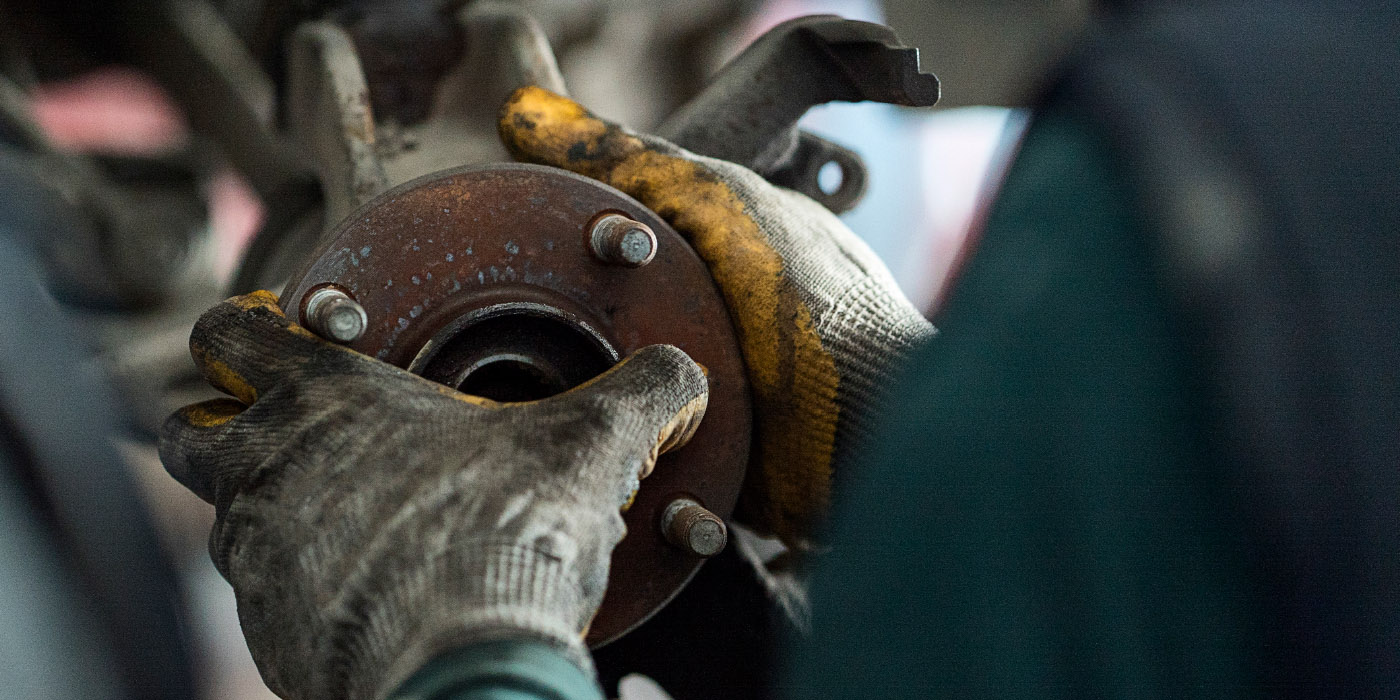
It is possible for a worn bushing to have alignment angles that are still within specifications. As the bushings fight against the forces of rolling resistance, braking and acceleration, weak bushings can cause the camber, caster and toe angles to change due to the size and placement of the bushings. This is why a visual inspection of the bushings can be critical. If any part of the bushing has separated or has been torn, it is grounds for replacement.
Ozone and extreme temperatures tend to destroy rubber bushings. Many bushings are subjected to high temperatures from the brakes. These temperatures can exceed engine and exhaust temperatures. Environmental damage of this kind will cause hardening of the materials and eventual cracking. As the cracks grow, they eventually will compromise the strength of the bushings.
Some cracking is normal. Mazda lists in its service information how long and how deep a crack can be before replacement is required.