Vacuum brake boosters will probably be with us for a long time. It is the most efficient and economical way to amplify the force exerted by the driver. But where the booster gets its vacuum is changing.
VW has been using vacuum pumps to power the brake booster on its diesel-powered vehicles for almost 40 years. Now, vacuum pumps are becoming more common on gasoline-powered VWs as well. The pumps supply a constant supply of vacuum no matter the engine speed or throttle position.
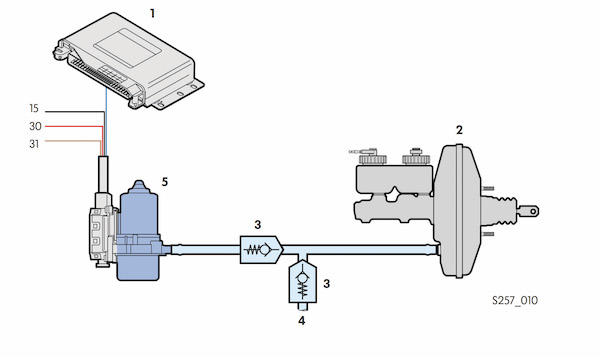
Why A Vacuum Pump?
In every piston engine, vacuum is generated during the intake stroke as the piston goes down in the cylinder and the intake valves are open. But VW engines have changed.
Increased efficiency has reduced the amount of vacuum available to the brake booster. Engines have been downsized to 2.0- and even 1.4-liters. This means that there is less displacement to generate the vacuum. Variable valve timing has further diminished the vacuum generated.
Turbocharging has also eliminated vacuum in the intake manifold. The turbocharger produces positive pressure or boost in the intake manifold. The only time an engine might be under vacuum is when the engine is decelerating, and the throttle is closed.
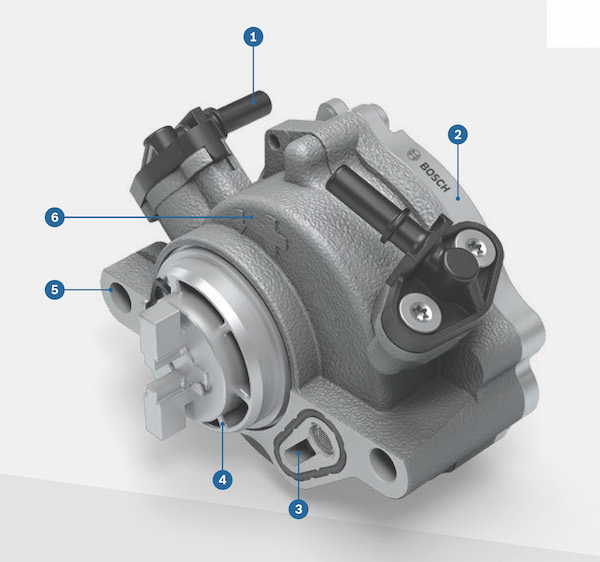
What Type Of Pump?
Vacuum pumps have been used on diesel engines for more than 40 years, typically as a diaphragm pump. These pumps were neither efficient nor reliable.
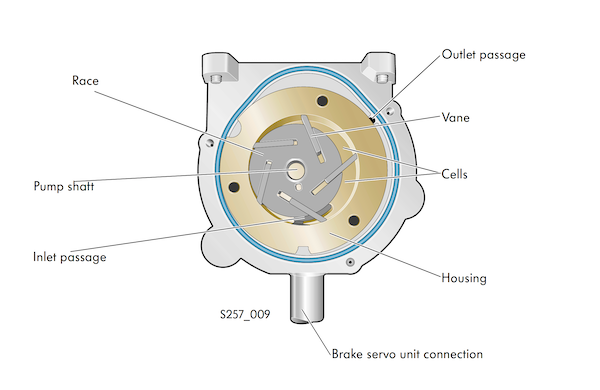
Most modern VWs use either an electric vacuum pump or a pump driven by a sprocket connected to the timing chain. These pumps use vanes attached to an offset shaft. As the shaft rotates, the vanes create a sealed chamber with the walls of the housing.
Since the shaft is offset, the chambers change in volume and produce a vacuum on the outlet side when turned. Electric pumps typically have multiple vanes; timing chain-powered pumps use just one vane.
Electric-powered vacuum pumps are controlled by the engine control module. The system uses a pressure sensor mounted between the pump and the booster. The ECM will look at the vacuum, brake pedal position and other engine parameters. The vacuum pump is controlled with a relay that is actuated by the engine control module. The pump is turned on for 2- to 3-seconds during startup.
Timing chain-powered pumps are lubricated with engine oil. The oil inlet is next to the shaft and is fed from the oil slung off the timing chain and sucked into the pump through a valve that controls the level of oil.
While it is rare for the vanes to wear out, it is possible for carbon and debris to enter the pump and cause damage to the vanes and housing. If the vanes can’t seal against the housing, a vacuum can’t be generated. The most common symptom of a worn pump is a hard brake pedal.
One of the most common pump problems is the rear cover leaking on the 2.5L five-cylinder engine. Some technicians have theorized that the leaks are caused because the cover and body of the pump are made of two different materials. The brake pedal will not be affected by the oil leak.
On 2.5L five-cylinder engine, the pump is positioned above the transmission. Often the pump will leak, and it appears the rear main seal is leaking due to the location of the pump. It is possible to replace the pump without removing the transmission. Most aftermarket vacuum pumps have an improved rear cover and seal.
The Booster
No matter if the booster gets vacuum from the engine or a pump, if it is damaged, the brake pedal performance will change. The condition of the diaphragm inside the booster is also important. If it’s cracked, ruptured or leaking, it won’t hold vacuum and can’t provide much power assist. Leaks in the master cylinder can allow brake fluid to be siphoned into the booster, accelerating the demise of the diaphragm.
If there’s brake fluid inside the vacuum hose, it’s a good indication that the master cylinder is leaking and needs to be rebuilt or replaced. Wetness around the back of the master cylinder would be another clue for this kind of problem.
To check the vacuum booster, pump the brake pedal with the engine off until you’ve bled off all the vacuum from the unit. Then hold the pedal down and start the engine. You should feel the pedal depress slightly as engine vacuum enters the booster and pulls on the diaphragm. No change? Then check the vacuum hose connection and engine vacuum. If it’s OK, the problem is in the booster, which needs to be replaced.