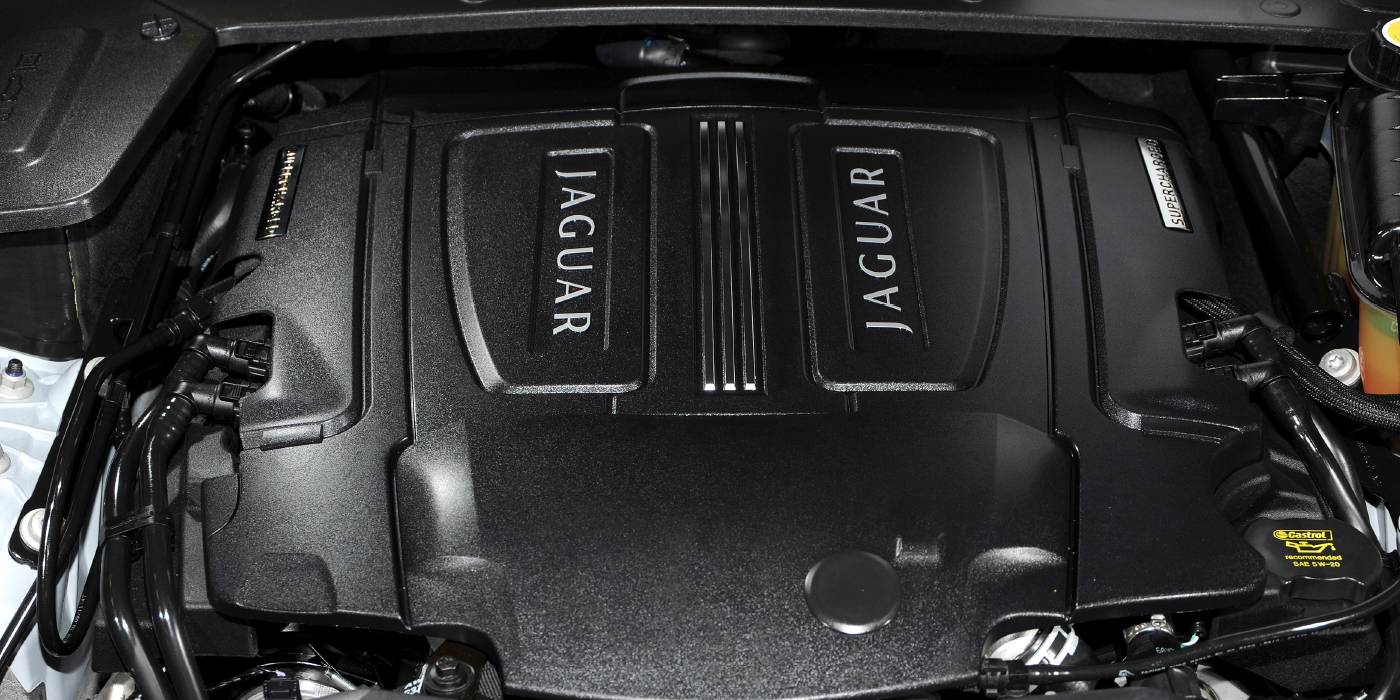
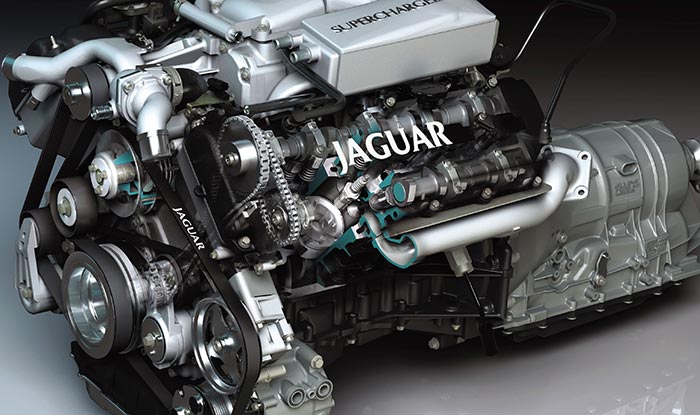
Jaguar and Ford introduced a new V8 in 1997. While it was not the most powerful DOHC V8 on the market, it was the most refined. Called the AJ-V8, the 4.0 L version produced 290 hp in naturally aspirated form and 375 hp with a supercharger.
During the first three years of production, the engine experienced timing chain and cylinder bore problems, most of which were resolved by 2002. A year later, Jaguar introduced the 4.2 L version that was a vast improvement over the 4.0 L engine, complete with a better valvetrain, block and cooling system.
Over the engine’s 12-year lifespan, Jaguar was constantly improving the AJ-V8 with better parts and software calibrations. However, in some cases, the changes in the engines were not consistent with the XJ, S-Type and XK in those same model years.
Jaguar has a strange way of designating the model year. A 2004 XJ might be considered a 2003.5 XJ if the VIN falls within a certain range. Also, changes to the engine might not correspond to a model year, but rather with a VIN or production date stamped into the engine. So, always have the VIN ready when ordering parts.
Check the Calibrations and Software
On almost all Jaguar V8 cars, there were at least five different engine control unit (ECU) updates and calibration changes. Some of these new calibrations were for models that were five or six years old.
Most of the updates concern poor idle quality, engine pinging and catalyst efficiency codes. New parameters recalibrate the fuel trims, engine temperature and ignition curves in order to increase longevity and solve common problems.
Take the time to determine if the ECU has the latest calibrations and reflash the firmware or software if necessary. Doing this before heading deep into a driveability problem can save you time and money.
Also, check the transmission control module for the latest calibration. Jaguar was always tweaking the shift parameters to increase the life and shift quality of the 5- and 6-speed ZF transmissions.
Timing Chains
The biggest issues with 1998-2001 models are the primary timing chains, guides and tensioners. On the early V8 models, the plastic guides can crack. This causes a lot of noise, vibration and jumped timing. The cracking of the guides is often attributed to neglected oil changes and a bad design. If the engine has a history of overheating, the guides could be damaged. Updated guides and tensioners with more robust die-cast components are available.
In late 2002, Jaguar switched to double-row chains and improved guides. This helped to reduce noise and increase longevity. The primary chains are lubricated using two squirt-jets directly mounted to the oil pump casing. If this jet becomes clogged, it can quickly lead to chain failure.
Even these newer engines are prone to guide and chain damage if the oil is not changed regularly. If you have serviced the timing chains, make sure to change the water pump, thermostat and thermostat housing.
 Variable Valve Timing
Variable Valve Timing
The 4.0 L engines are equipped with helical gear variable valve timing actuators on the intake camshafts that could change the timing by 30 degrees. They can be very robust, but can also suffer if the oil is not changed regularly.
For the 4.2 L engines, the VVT units use a vane device to control the camshaft angle. The system operates over a range of 48 degrees and is advanced or retarded to the optimal angle within this range. The engine control module controls the VVT using engine control signals pertaining to engine speed and load, and engine oil temperature to calculate the appropriate camshaft position. The VVT camshaft position sensor provides feedback control on the intake camshaft’s position relative to the position of the crankshaft and exhaust camshafts.
If engine oil pressure is below 1.25 bar (18 psi), the VVT units will not operate because there is insufficient pressure to release the unit’s internal stopper pin. This usually occurs when the engine is shutting down and the VVT has returned to the retarded position. The stopper pin locks the camshaft to the VVT unit to ensure camshaft stability during the next engine startup. If the unit or stopper pin is damaged, it will cause a rattle during startup.
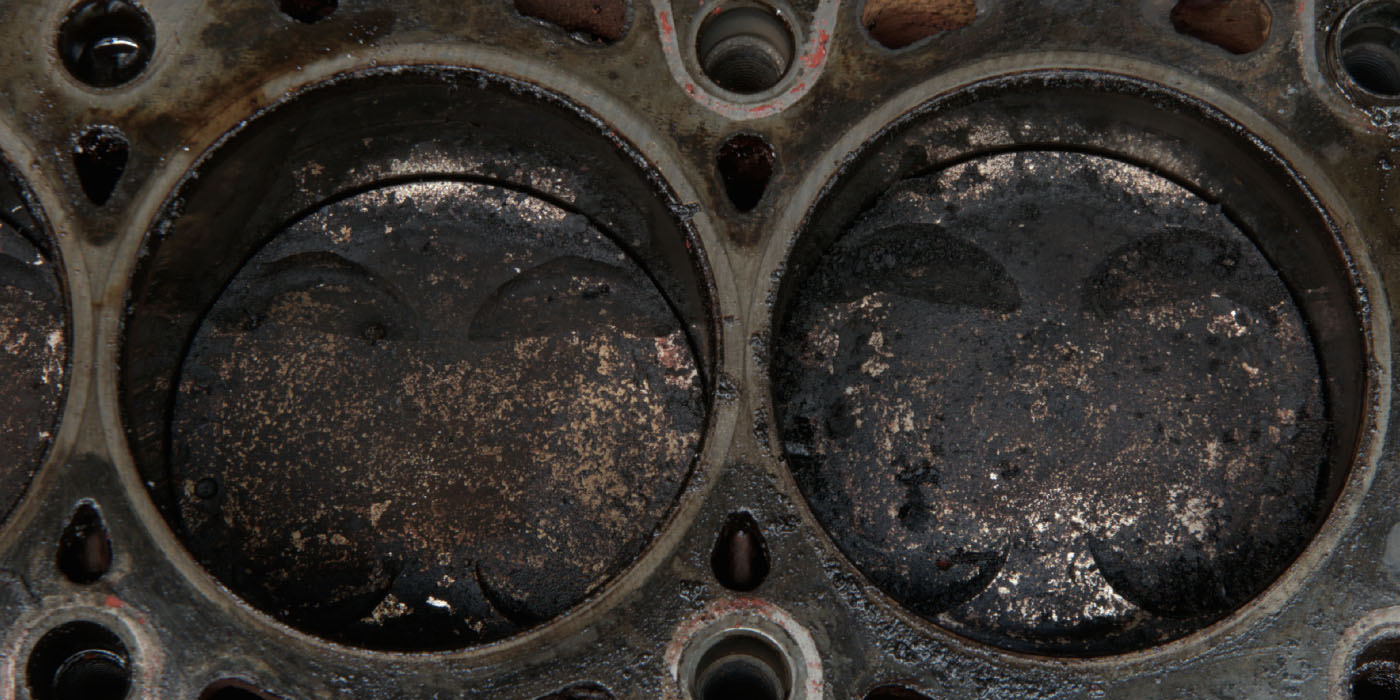
No Compression
For its 1998 and 1999 V8s, Jaguar used Nikasil coatings on the engine cylinder walls instead of liners. Nikasil is a very hard, friction-reducing material made of nickel, silicon and carbon. Porsche and other manufacturers have used Nikasil coatings with very few problems for more than 25 years.
The problem with the early Jaguar V8s is two-fold. First, the Jaguar V8 runs cool and is very under-stressed. If the engine is not allowed to heat up to full temperature, condensation or water can build up in the oil. Second, if the owner is frugal and uses regular or low-quality gas, the higher levels of sulfur in the fuel can combine with the water, which can produce sulfuric acid when combined in the crankcase and combustion chamber.
This acid can destroy the Nikasil coating on the cylinder walls. The main symptom of this condition is a loss of compression in all cylinders. The customer may complain of a loss of power and hard starting. This condition is rare, but it is possible that fuels with higher ethanol concentrations might also damage Nikasil engines.
 Erratic Gas Gauge
Erratic Gas Gauge
A customer may complain of erratic gas gauge readings.
Oftentimes, the driver will get a low fuel warning when first starting the vehicle in the morning and the gauge will read low. After a certain amount of driving, the fuel level will return to normal.
This could explain why. XJ and S-Type models have saddle-style fuel tanks that surround the driveshaft. Each tank has a fuel level sender, but one tank has a supply/transfer pump and the other has the primary fuel pump that supplies fuel pressure to the engine. The supply/transfer pump moves fuel to the primary tank so the fuel pump is always submerged.
On later vehicles, a Rear Electrics Module (REM) manages the fuel transfer and tank levels using the two sender units. It takes the information from the two senders to calculate the fuel level that is shown on the gas gauge. But often an open or damaged sender will cause erratic readings.
Below is a quick way to check the operation of the sensors without having to access the fuel pumps.
1. Open the driver door.
2. If possible, check the instrument cluster and REM for codes including: B1202, B1204, B2627 and B2628. Write down the codes and clear them from both modules. In some cases, you will not be able to complete the rest of the steps if the codes are present.
3. Place the instrument cluster into test mode by pressing the trip button in and holding it while turning the ignition to the ON position. Release the trip button five to eight seconds after the ignition switch is turned turn.
4. Scroll using the button on the end of the left stalk until you reach the RAW1 signal.
5. Rock the vehicle and view the reading. You will see a variation in the reading. A good reading should be between 27 and 240. If a reading of 255 is displayed at any time, it indicates an open circuit.
6. Scroll to the RAW2 signal displayed on message center by pressing the trip button.
7. Repeat the procedure outlined in Step 5.
On the bench, both senders should have a range between 15- and 160-ohms. Fuel level sender information obtained through the use of a scan tool can also be used to determine if the transfer pump is working.
Vacuum Leaks
If you get a car with a rough idle, poor shifting and code for misfires and lean conditions, check the vacuum line connections at the throttle body. This is the leading source of vacuum leaks on this engine. Another area of concern is the PCV valve on 4.2 L engines. Often the valve can get stuck in the open position and cause a rough idle.
Transmission Leaks
On 2004 models with the six-speed ZF automatic transmission, the most common areas for leaks are the wiring connection for the valve body and the rear output seal. When refilling the transmission, follow the recommended procedures, which may take 30-40 minutes, in order to get the transmission up to temperature.
Misfire Monitors and the Driveshaft
If the driveshaft is out of balance or damaged, the crank angle sensor might pick up on these vibrations. This can suspend misfire monitor testing and prevent the monitor from completing the emissions monitor test. If you have a vehicle with random misfire codes but no detectable misfires, check the driveshaft balance.