The 2004-2009 Mazda3 is based on the Ford global C1 platform, shared with the European Ford Focus and Volvo S40. Nothing is really groundbreaking about the brake system. But, not paying attention to the details can end in a post brake job comeback.
The 2004-2009 Mazda3 is based on the Ford global C1 platform, shared with the European Ford Focus and Volvo S40. Nothing is really groundbreaking about the brake system. But, not paying attention to the details can end in a post brake job comeback.
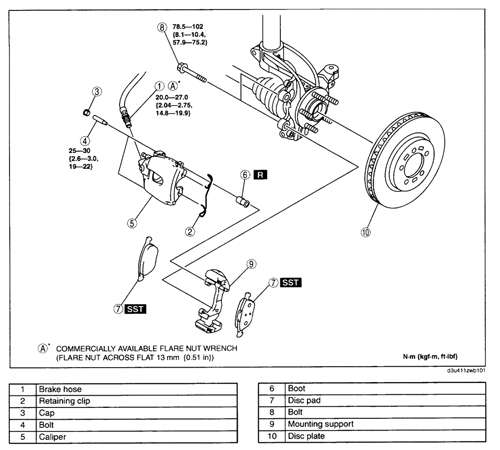
Front Brakes
Pads should be replaced when there is 2mm or less of friction material. The rotors have enough material on them to last at least one turning on the lathe. The runout specification for these vehicles is .002” and disc thickness variation should be far below .0005”.
 Mazda claims repeated panic braking may raise the temperature in some portions of the disc plate by approx. 1,000°C (l,832°F). This temperature is almost near impossible to achieve this side of a high-speed police chase.
Mazda claims repeated panic braking may raise the temperature in some portions of the disc plate by approx. 1,000°C (l,832°F). This temperature is almost near impossible to achieve this side of a high-speed police chase.
The calipers mount to the brackets using caliper guide pins with Allen heads. The sleeves and boots should be disassembled, cleaned and lubricated every time the brakes are replaced. The torque for the guide pins is 21 ft/lbs and the caliper bracket bolts should be tightened to 75 ft/lbs.
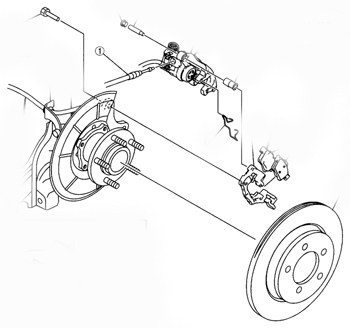 Rear Brakes
Rear Brakes
All Mazda3 models have rear disc brakes. The calipers mount to the brackets using caliper guide pins with Allen heads. The sleeves and boots should be disassembled, cleaned and lubricated every time the brakes are replaced. The torque for the guide pins is 21 ft/lbs and the caliper bracket bolts should be tightened to 55 ft/lbs.
Mazda uses a hand-brake that is incorporated into the rear caliper. They use a couple of systems to retract rear pistons. The later-model cars require the familiar method of turning the piston clockwise while applying pressure, where others will have a plug on the back side of the caliper that provides access for an Allen wrench to facilitate retracting the piston, but be careful as you retract the piston.
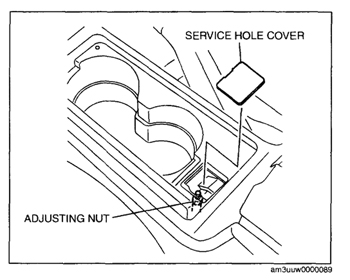 After the pads are replaced, pump the pedal and adjust the parking brake mechanism in the rear calipers. If the level has too much travel, perform the following steps:
After the pads are replaced, pump the pedal and adjust the parking brake mechanism in the rear calipers. If the level has too much travel, perform the following steps:
1. Pump the brake pedal a few times.
2. Remove the service hole cover of the rear console.
3. Turn the adjusting nut and adjust the parking brake lever.
4. After adjustment, pull the parking brake lever one notch and verify that the parking brake warning light illuminates.
5. Verify that the rear brakes do not drag.
ABS/DSC Diagnostics and Repair
The Mazda3 comes in two flavors, ABS and ABS with Dynamic Stability Control. Both systems connect to other vehicle components via a high-speed serial data bus. The DSC system ties more components together like a yaw/pitch sensor and steering position sensor onto the bus.
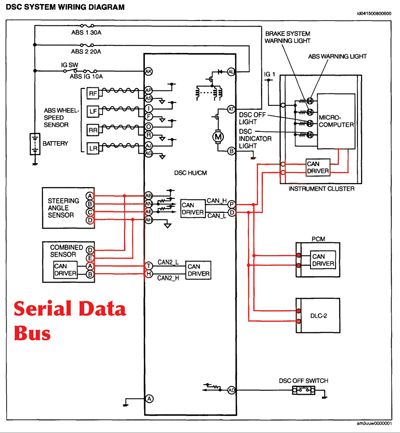 If you are seeing communication-related DTCs, it is essential that you fully diagnose problems with the system before you start replacing sensors and modules. Some of these vehicles have been on the roads for more than six years and the connections are starting to corrode and fret.
If you are seeing communication-related DTCs, it is essential that you fully diagnose problems with the system before you start replacing sensors and modules. Some of these vehicles have been on the roads for more than six years and the connections are starting to corrode and fret.
One of the main culprits of ABS/DCS problems are the connectors, especially under the hood where the control/modulator unit connects. Being able to measure values at the connectors and observe data on a scan tool is essential for diagnosing problems.
If a modulator/control unit is replaced, the pressure sensors must be re-calibrated with a scan tool that is able to communicate with the chassis/ABS module. If this is not performed, it can result in brake failure and lock up.
If you have DTCs C1141, C1142, C1143, C1144, C1233, C1234, C1235 or C1236 (ABS wheel-speed sensor/ABS sensor rotor), chances are something is wrong with the wheel bearings. Another cause for these codes could be an accumulation of metal debris on the sensor. The front bearings are press-in cartridge-style units. Rear wheel bearings are hub units. In the front, the tone ring, or encoder, is on the inner seal of the bearing and the sensor is mounted in the knuckle. The parameters for these codes to be set are abnormalities in the signal like a weak signal or large differences in the value when compared to the other sensors.
If you have DTCs C1145, C1155, C1165 or C1175 (open sensor), it could be damaged wiring or a failed sensor. If you have more than one, chances are there is a problem with the connection at the control unit or in the front or rear harnesses for the sensors.
These DTCs will usually clear themselves after repairs are made and the vehicle is driven above 6.2 mph when the self-diagnostic check is performed.
Some customers may report a slight clunk, bang or jolt from the front of the vehicle. This concern will most likely occur during the vehicle’s first forward movement, and after the vehicle sits for a few hours and/or a cold soak. This is a normal operating noise of the ABS system.
If you encounter a customer complaint for this concern, explain that the noise comes from the ABS/TCS/DSC “Malfunction Detection Function” initial check. The initial check is a necessary function to ensure the normal operation of the ABS/TCS/DSC system.
This initial test function occurs during the vehicle’s first forward movement and when the vehicle reaches approximately 6.2 mph.