Let’s face it, modern vehicles are more dependent on electrical systems than ever before. These days, it seems that you can’t turn on a heated seat, turn on a light, or roll down a window without one or more control units communicating with one another.
This of course presents a tremendous challenge for future vehicles, as we may soon reach the upper limits of the 12V electrical system we know today. The more electrical systems we put into our vehicles, the more likely it is that the battery and charging system won’t be able to keep up.
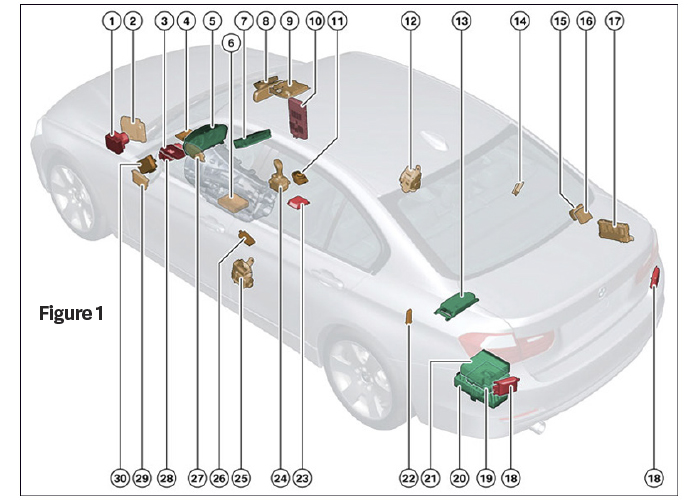
In fact, a modern luxury vehicle such as the BMW F30 3-Series may have 100+ actuator motors and control units, all of which need to be supplied with power (Figure 1). Power consumption is still considerable even when the ignition key is off; this is commonly known as “parasitic drain.”
To meet these increasing energy demands, the engineers at BMW needed to develop a more powerful battery solution. This new battery would need to be more powerful than comparable Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) or lead-acid batteries, with better stability and service life. It needed to weigh the same, if not less, than other batteries so that it wouldn’t negatively affect the sporty drivability for which the brand is known.
So, BMW started offering lithium-ion batteries in its F80 M3 and F82 M4 in early 2014. These batteries didn’t gain a lot of attention and have “flown under the radar” in the few years since. Customers likely don’t know which type of battery they have, and technicians likely won’t know either without learning how to identify them. Let’s dig into this type of battery construction, and what it has to offer.
Why Lithium-Ion?
Lithium-ion batteries offer a few notable advantages:
- They’re maintenance free;
- They weigh less than AGM or lead-acid batteries (as much as 50% less);
- They offer higher current consumption, which means they can achieve a higher state of charge under load;
- They offer increased cycle stability, and higher current consumption which results in faster charging (w/proper equipment);
- They’re able to completely cycle around 14x more than a conventional lead-acid battery, making them suitable for use with the automatic engine start/stop function (MSA) in conjunction with the intelligent generator control (IGR);
- The battery life is about double that of a traditional lead-acid battery;
- They’re safe – lithium iron phosphate cells (LiFeP0₄) generally have a lower hazard potential than other lithium-based batteries.
How to Identify a Lithium-Ion Battery
Lithium-ion batteries are easily distinguished from AGM or lead-acid batteries thanks to a few key traits (Figure 2):
- LIN bus connection inside of the lid (for communication with the Intelligent Battery Sensor (IBS);
- “Li-ion” notes on the top of the label;
- Large vent connection in the lid.
The lithium-ion battery has an integrated electronic disconnect switch for protection. This could be triggered by overvoltage, undervoltage, high temperature (< 80°C), or a short circuit.
Lithium-ion batteries have a black case housing just like other batteries, but the “Magic Eye” is not present on top of the lid.
Internal Construction
Lithium-ion batteries may appear similar to other batteries on the outside, but on the inside they’re much different. The most notable difference is that they contain only four cells, with a nominal voltage of 3.3V each, for a total nominal voltage of 13.2V overall.
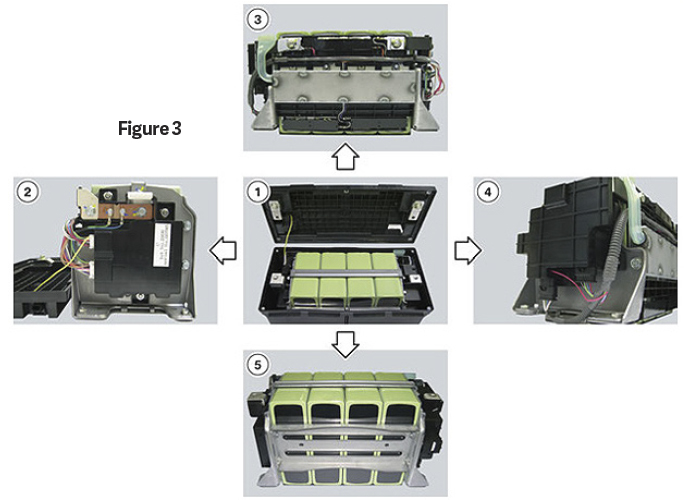
Using Figure 3 for reference, locate the following components inside the lithium-ion battery:
- Inner structure;
- Battery supervision circuits (BUE) with precision resistor;
- Metal ventilation chute;
- Electronic disconnect switch (two relays);
- Four li-ion battery cells.
The integrated BUE is responsible for a number of tasks, including communication and wake-up function via LIN data bus, and monitoring the voltage and current supplied by individual cells and the battery overall. It also monitors closed-circuit current, battery temperature, internal resistance, state of charge, battery condition, battery capacity, and data memory for battery information. Finally, it is responsible for activating the battery isolating switch if a fault is detected.
All of these data points are accessible with a scan tool which is capable of communicating with the BMW CAN or LIN bus.
How Do I Charge a Lithium-Ion Battery?
There are new requirements for charging lithium-ion batteries by the BMW group. Charging voltage and trickle charging voltage must be closely monitored or adjusted to avoid damaging the battery or the BUE.
BMW recommends the use of one of the following chargers:
- DEUTRONIC DBL800/1200/1600
- ELTEK MultiCharger 750/900/1500
- ELEKTRON HS-1000
BMW states that you must use the charging points in the engine compartment to prevent the BUE from malfunctioning. Existing chargers which are designed for lead-acid or AGM batteries will generate a charging voltage that is too high for the lithium-ion battery. If the charging voltage is too high, the electronic disconnect switch can open, which generates a message in the instrument cluster.
Before charging a lithium-ion battery, adjust the charging voltage; it must not exceed 14.0V. This applies whether charging the battery in or out of the vehicle. The lithium-ion battery should be charged only at a battery temperature of > 5°C.
How Do I Test/Replace a Lithium-Ion Battery?
The integrated BUE is capable of monitoring and testing the battery for faults. Lithium-ion batteries cannot be replaced with other construction types. This is because the BUE would not be recognized by the LIN bus, and fault codes would occur.
Removal and installation of the battery is nearly identical to other types of batteries. Be careful whenever disconnecting or connecting the battery vents and the LIN bus electrical connector to avoid damaging them.
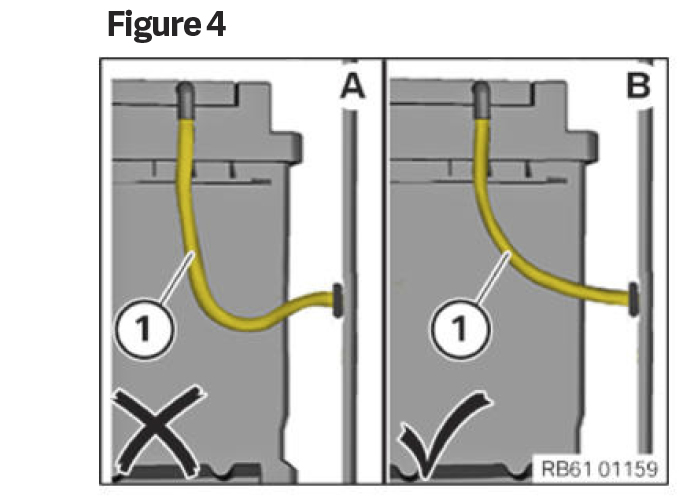
Use a torque wrench to tighten the battery terminals to specification. Ensure that the vent hose (#1 in Figure 4) is sloped outside of the vehicle to avoid the risk of siphoning.
Once the new battery has been connected to the vehicle, use your scan tool to register the new battery with the Battery Energy Management Systems (BEMS). This way the system will recognize the battery size, amp rating, etc. This may require you to enter a code located on a sticker on top of the battery.
Is Lithium-Ion the Battery of the Future?
The lithium-ion battery is lightweight, powerful, and boasts an impressive service life. However, it comes at a significantly higher retail price compared to AGM or lead-acid batteries, and it requires specialized scanning and charging equipment in order to service it. Only time will tell if this type of battery construction will gain traction in the industry, but it’s certainly something to keep an eye on!