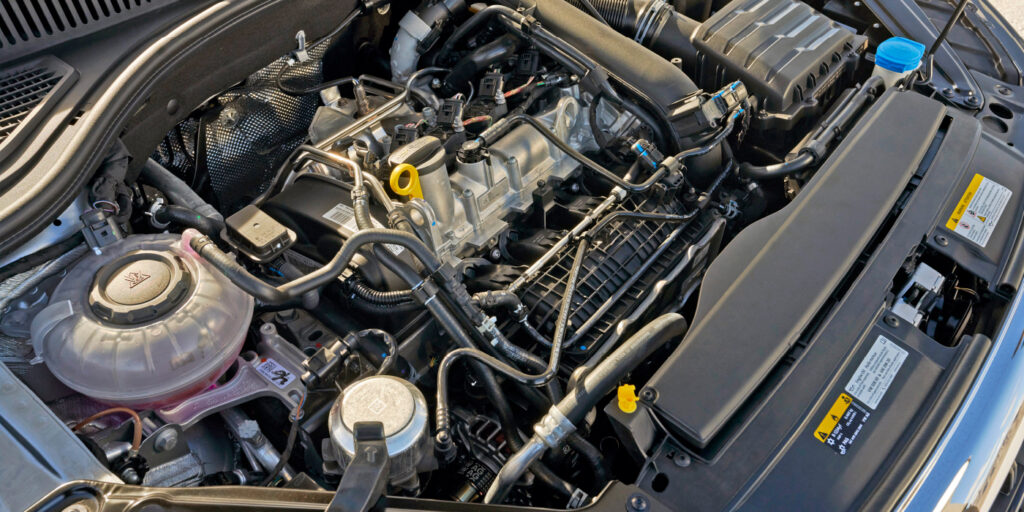
The 1.4L turbocharged EA211 engine has been around for about a decade now, and it was standard equipment on several Volkswagen models here in the U.S., including the MK7 Golf and the Jetta Hybrid. This compact but powerful engine replaced the naturally aspirated 2.5L five-cylinder engine. It makes a respectable 140 hp, but it makes a stout 184 lb.-ft. at an astonishingly low peak of 1,400 rpm. That means that peak torque is available practically from idle, making this engine the perfect powerplant for the typical “daily driver.”
This engine focuses on fuel economy above all, and it is exceedingly good at it. It’s lighter than other 4-cylinder VW engines, thanks to its all-aluminum block construction, which sheds around 42 pounds. Thanks to lighter connecting rods and crankshaft counterweights, the engine is 49 pounds lighter overall and as much as 20% more fuel efficient, according to VW.
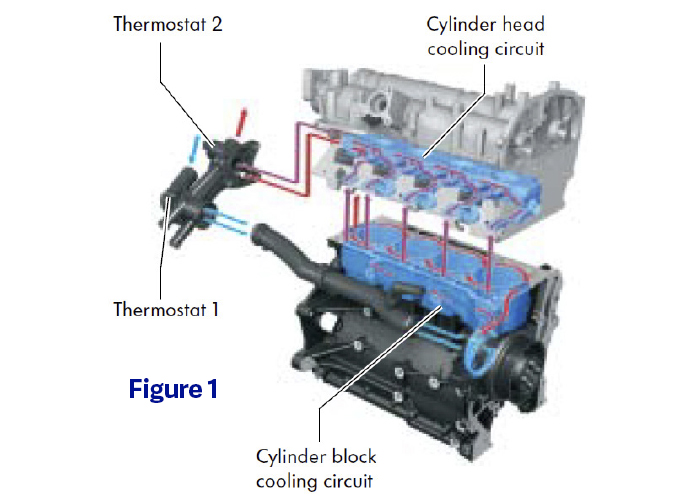
Another notable innovation on this engine is the fact that the exhaust manifold is incorporated into the cylinder head (Figure 1). This reduces the distance between the exhaust valves and the turbocharger, saves weight and helps to heat up the catalytic converter faster, reducing tailpipe emissions.
The manifold is surrounded by coolant jackets that help the engine to reach operating temperature faster and provide warm air inside the cabin quicker than ever before. This coolant circuit is isolated from the rest of the system, but we’ll talk more about that later.
Technical Service Bulletins can be very valuable for techs and vehicle owners who may notice a particular symptom on a vehicle. They also can be used to identify a pattern failure, or a common symptom that is seen by many vehicle owners over time. However, there are very few TSBs which apply specifically to the EA211. Let’s take a look at some unique features of this engine family, as well as a few issues that you may come across.
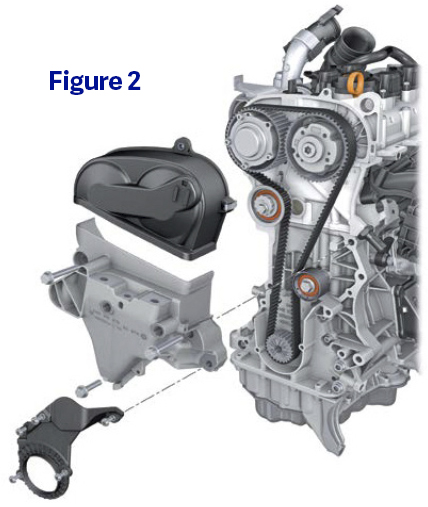
Timing Belt
Yes, you read that right, VW has gone back to timing belts on this engine (Figure 2). Now I know what you may be thinking; this is not the same belt that we saw installed on the older 1.8T engine in the MK4 GTI. The belt drive means less friction loss compared to a chain drive, and VW says that it’s good for the lifetime of the engine. It’s true, you won’t find “replace timing belt” called out anywhere on the maintenance chart. This may make some of us just as nervous, like when other manufacturers started calling their transmission or differential oil “lifetime oil,” but we’re hoping that VW has done the work and these belt drives will last a long time.
So, what could shorten the service life of a timing belt? Aggressive tuning, which raises the rev-limiter, or oil or coolant intrusion inside the timing cover from a leaking gasket or hose, immediately come to mind. It would be wise to include a visual inspection of the timing belt around the 100,000-mile mark to help keep the engine running for years to come.
Air-To-Water Intercooler
Say goodbye to the air-to-air intercooler and hello to the new air-to-water heat exchanger. This new intercooler is integrated directly into the intake manifold, making the engine even more compact. It also has the added benefit of reducing the distance the charge air needs to travel from the turbocharger to the cylinders.
Spin-On Oil Filter
Oil changes are easier on the EA211 compared to the 1.8L or 2.0L EA888. No special tools are required for this job, thanks to the traditional spin-on oil filter on the front of the engine and the steel drain plug (not plastic like the EA888).
Potential Coolant Leak #1: Thermostat & Water Pump Assembly
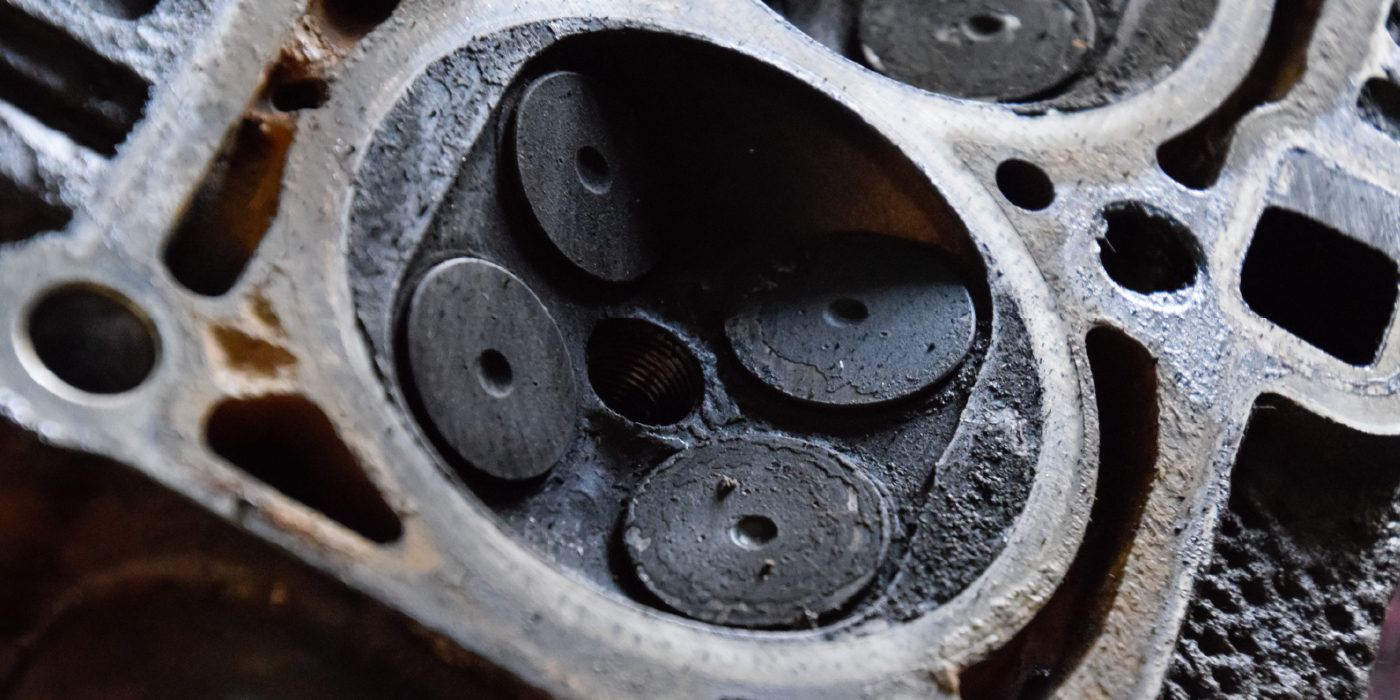
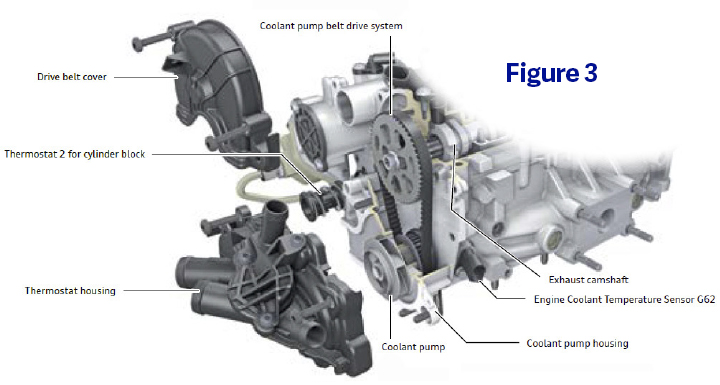
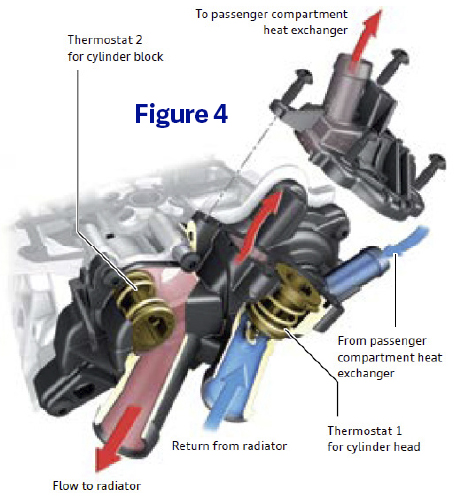
The water pump on this engine is driven by a small-toothed belt on the back side of the exhaust camshaft (Figure 3). This belt is located behind a plastic cover, over the transmission case on the cylinder head. There is a large thermostat assembly that is bolted to the outside of the water pump. This thermostat assembly houses two different thermostats; one to manage coolant flow for the engine block and another to manage coolant flow for the cylinder head (Figure 4).
These plastic thermostat assemblies have been known to fail or leak prematurely if they come into contact with engine oil, sometimes from a leaking PCV assembly. It’s important to watch for any signs of coolant leaking in the area of the thermostat assembly and advise your customer accordingly.
The water pump drive belt could also fail due to oil contamination. This would result in a complete loss of coolant flow, and the engine would overheat quickly.
Potential Coolant Leak #2: Coolant Pipe
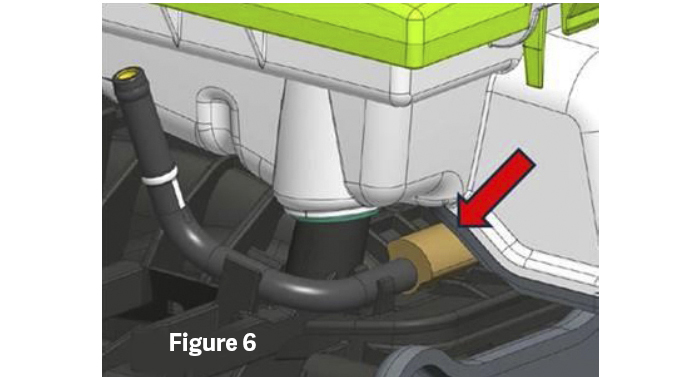
The coolant pipe, which runs underneath the air box, may be damaged and leak. This is caused by the pipe rubbing up against the bottom of the air box (Figure 5).
Replace the coolant pipe with the updated pipe assembly (part number 04E 121 064 S), which features an insulation wrap for protection (Figure 6).
The Test of Time
So far, this engine has aged well and is proving to be quite reliable over time, assuming it’s properly maintained, of course. We’ll continue to keep our ears to the ground, and if we find a pattern failure, you’ll see it in a future article.