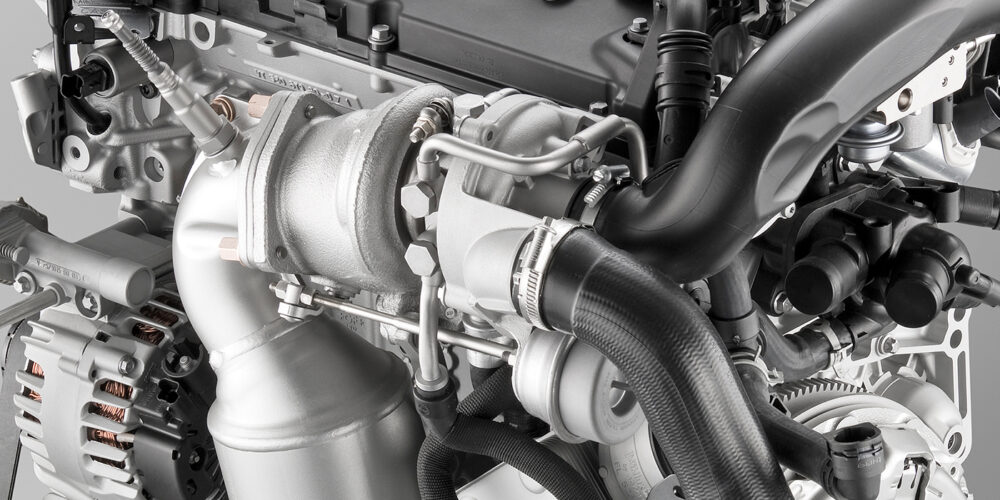
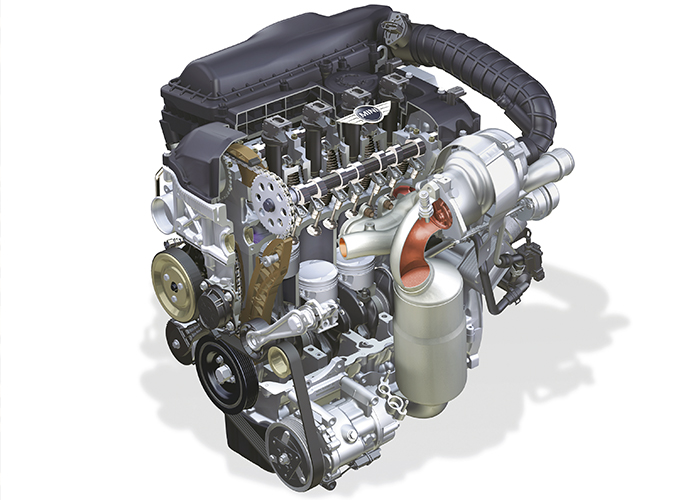
In 2006, BMW modified the MINI Cooper from having a supercharged engine to a turbocharged engine. The supercharger had issues with internal wear that could cause bearings and gears to fail. The turbocharger has proved to be more reliable. But, as the years have passed, the one problem that has surfaced is what can happen when the owner does not maintain their vehicle with regular oil changes.
No matter if it is a BMW or MINI, when the engine stops turning, the oil flowing to the turbocharger stops. The oil inside the turbocharger might drain out of the center section through the return line. The remaining oil in the center section is heated to the point where it is turned to carbon deposits. Carbon deposits can obstruct the passages that carry oil to the turbine shaft and bearings.
OIL AS COOLANT
When the engine is running, the oil is a coolant that draws heat out of the turbocharger. But, for the oil to cool the turbo, it must flow. Restrictions in the oil feed or return lines can cause the turbocharger to operate hotter than normal The most common restriction for turbochargers are not blockages in the feed line, but elevated crankcase pressure.
The return line on most engines is plumbed into or above the oil pan. If crankcase pressures are high due to blowby or a restricted PCV system, the oil coming from the turbocharger will have to overcome the pressure to drain into the oil pan. This pressure can limit the flow of oil to cool the turbocharger.
Oil that is certified by an OEM for its turbocharged engines can handle the heat. NOACK testing is performed by heating the oil to 250˚C for one hour under a constant flow of air. The oil is weighed before and after the test. When oil evaporates, it leaves behind carbon and sludge that can damage the turbo and engine. The lower the NOACK number means less oil has evaporated. Also, some manufacturers might give an “ash point” temperature for the oil. This number is the temperature at which the oil evaporates when exposed to heat. For turbocharged engines, the higher the flash point means it will not break down when pumped through the hot center section.
ENGINE COOLANT AS TURBO COOLANT
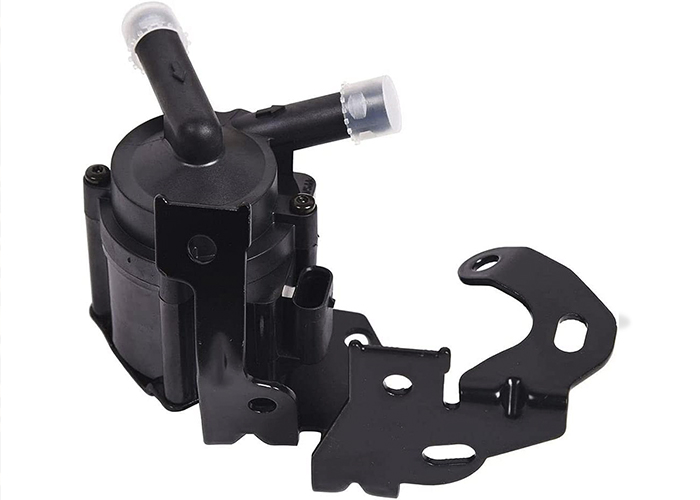
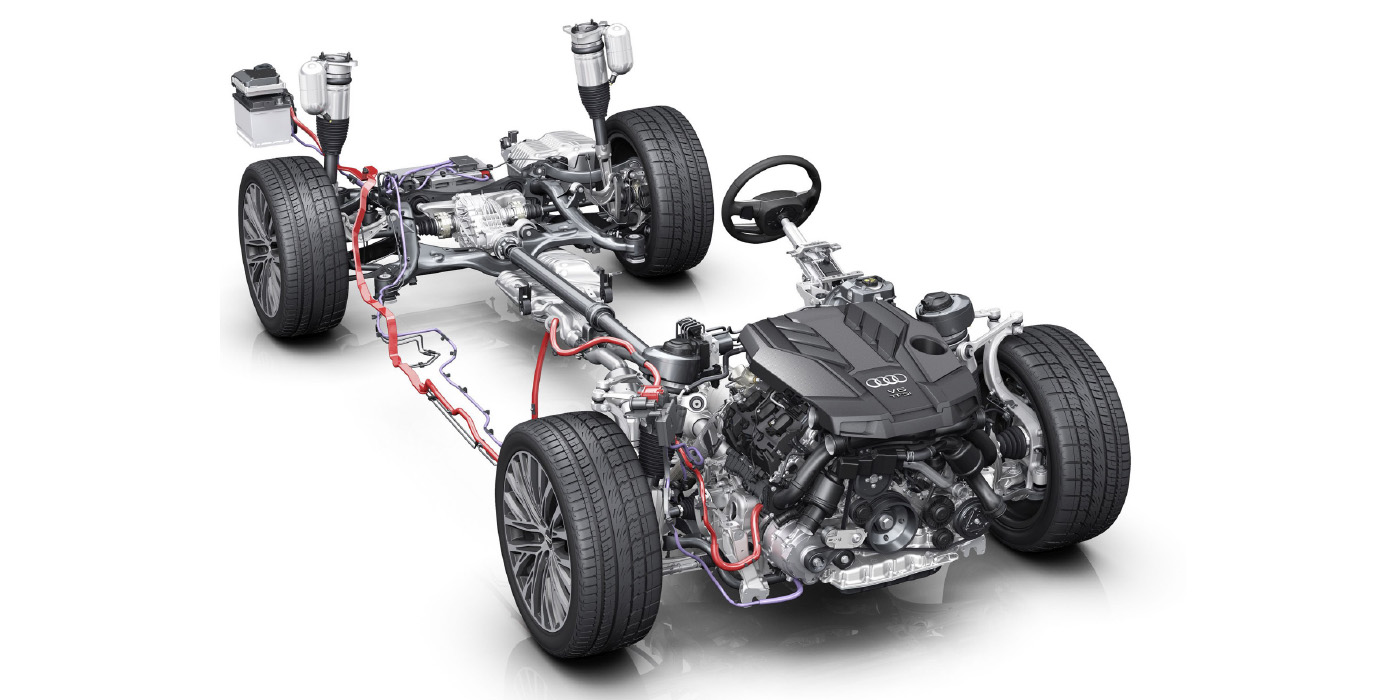
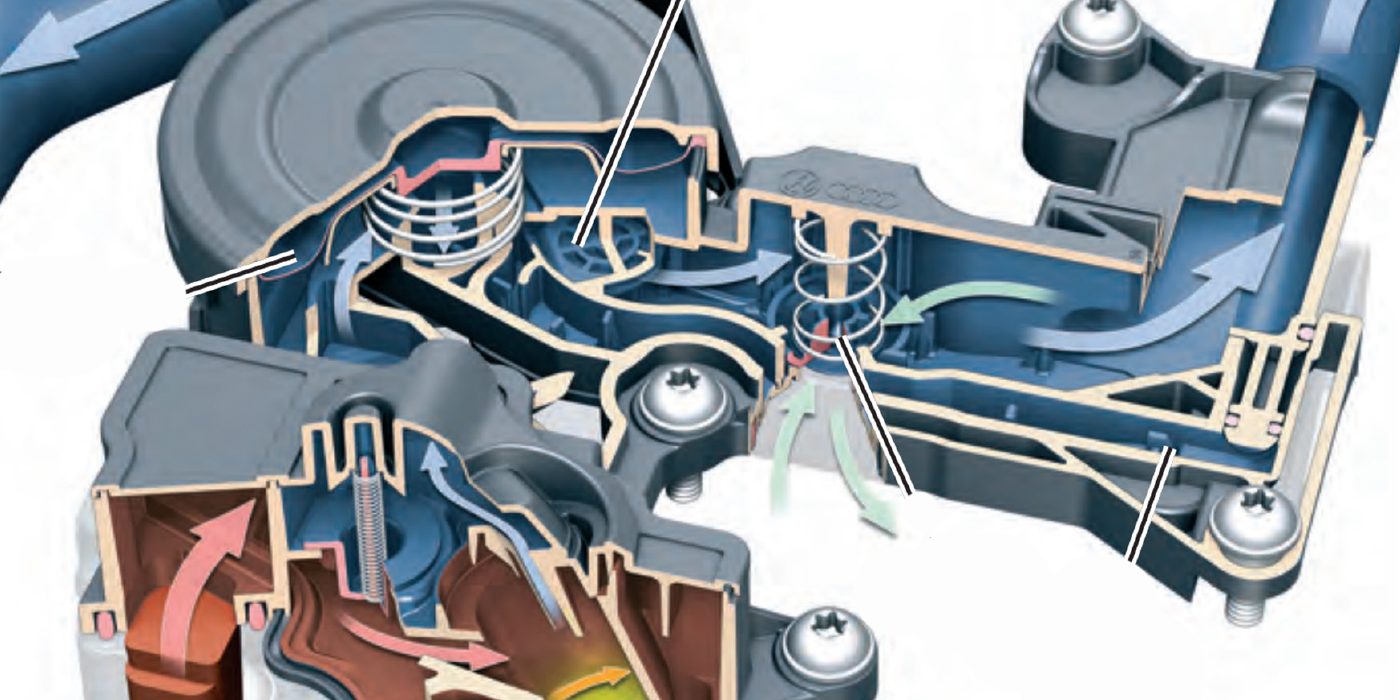
If you were to listen to a MINI or BMW car when the engine is shut down, you might hear a faint buzzing noise. This noise is an electric pump circulating engine coolant through the turbocharger’s center section for 2 to 15 minutes after the engine stops turning.
The circulating coolant helps to cool the turbocharger. Most pumps will free-spin when the engine is running and engage when the engine is shut off.
The run time and speed of the pump is determined by many factors. Most systems look at the coolant temperature of the engine using sensors mounted in the head, block and radiator. Once a sufficient drop in temperatures is measured, the pump will be shut off. Some systems will also look at previously calculated load and throttle position before the key was removed from the ignition to determine cooling pump run times.
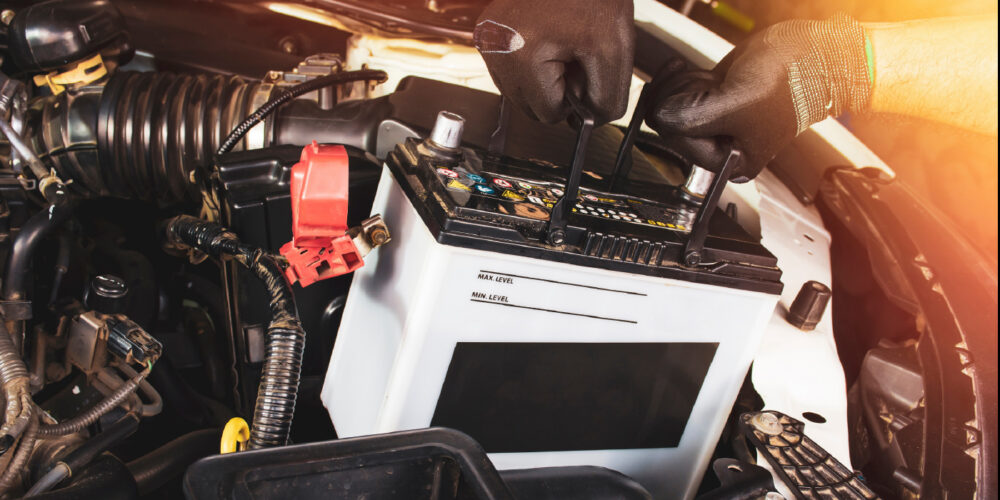
Many engine management systems look at battery voltage to determine how long the pump can run to cool the turbocharger. Most sophisticated systems use the battery life monitor that measures the current draw through the positive battery cable. Most systems will prioritize cranking and starting the engine over cooling the turbocharger in situations where the battery is marginal.
When selecting a battery, it is still critical that the cold-cranking amps match, but it is vital the reserve capacity (RC) of the new battery meets or exceeds the specifications of the original battery. Turbocharged applications need more reserve capacity in the battery due to higher key-off battery loads.