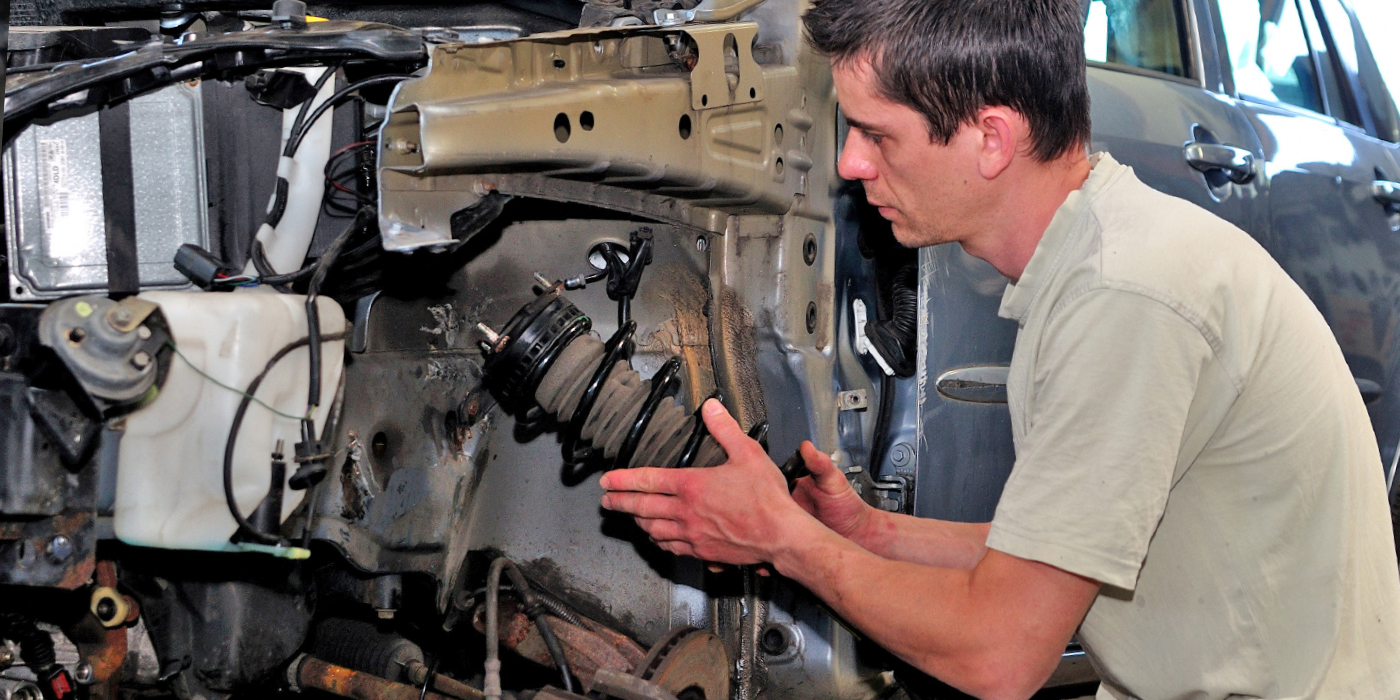
Often-overlooked engine components that may need to be replaced when installing a remanufactured engine are motor mounts. These rubber mounts can deteriorate, collapse and/or separate with age. Fluid-filled “hydraulic” type mounts can often leak, allowing annoying engine vibrations to be transmitted to the chassis.
Most mounts are designed so that separation won’t allow the engine to fall out onto the roadway. But a bad mount may cause a myriad of problems — many easily misdiagnosed. Often, bad motor mounts allow the engine to rock and move around, causing noise and interference problems with the throttle, transmission and clutch linkages. For example, a thumping noise when the transmission is put into gear or when the vehicle is accelerating is a classic symptom of a bad mount.
Excessive engine rocking also can create exhaust leaks and rattles where the head pipe joins the exhaust manifold. Plus, the donut that seals the exhaust joint can be crushed or broken by the motions of the engine, or the head pipe or pipe flange may crack.
Cracked or broken motor mounts can be an annoying source of vibration and noise, typically a clunk or shudder when accelerating hard. A broken or separated mount may even allow an engine-driven fan to scrape the fan shroud or contact the radiator, which also contributes to annoying noise.
Because motor mounts maintain engine and driveline alignment in FWD cars and minivans with transverse-mounted engines, it’s important that the mounts be in good condition. The mounts support the engine and transmission or transaxle, and help dampen noise and vibration to isolate the powertrain from the rest of the vehicle.
The upper mounts on FWD applications also help control engine rock as the engine applies torque through the driveshafts. While the design of the mount may prevent the engine from literally falling out of the car, it won’t keep the engine from twisting or hopping on its mounts every time the vehicle accelerates or is under load, which can produce thumping and rattling noises. It also can overstress components such as radiator and heater hoses, wiring connectors and the exhaust system.
A broken or loose motor mount in an FWD application can be even more serious because it may allow engine movements that interfere with the throttle or shift linkage. If the bad mount is an end mount, it may also contribute to a torque steer condition and cause accelerated wear or separation of the inner CV joints on one or both driveshafts. The noise produced by a separated or broken motor mount often sounds like a bad U-joint or inner CV joint (a clunk when accelerating or placing the transmission or transaxle in gear). So before either of these other components are replaced, the mounts should be checked.
Some mounts are “hydroelastic” and have hollow chambers filled with hydraulic fluid to dampen vibrations that would otherwise be transmitted across the mount to the chassis. Motor mounts need to be replaced when they’re loose, broken or collapsed. And, replacement mounts should be the same (fluid-filled hydroelastic or solid rubber) as the original.
Caution: Substituting a less expensive solid mount for a fluid-filled mount can increase the transmission of engine noise and vibration to the rest of the chassis. These mounts may save your customer a few bucks, but won’t do the same job as the original. They feel harsher and transmit more noise and vibration to the rest of the vehicle, and ironically, may cause a customer to return with complaints of a harsh rides or vibration.