Push button keyless start systems began appearing on several import cars about six years ago, and are now being offered on more and more new vehicles, both import and domestic. Motorists say they like the push button keyless start systems because they are convenient to use. There’s no ignition key or switch to fumble with, and you don’t have to do anything other than have the smart fob in your pocket or purse when you get in the car. Just put your foot on the brake pedal (or depress the clutch pedal if the vehicle has a manual transmission) and push the Start button to start the engine (or activate the powertrain if the vehicle is a hybrid).
There’s also a certain amount of “cool” factor involved. Pressing on a red (or gray or black) Start button is kind of like pressing the launch button for a rocket. For those who own older vehicles that don’t have this cool bit of technology, there are aftermarket conversion kits that allow a push start button to be installed. These kits are not true keyless start systems because there is no smart fob. Instead, the starter motor solenoid circuit is wired through the start button. The vehicle owner still has to insert a key into the ignition switch and turn it to unlock the steering column and deactivate the immobilizer system.
HOW THESE SYSTEMS WORK
Basically, a keyless push button start system eliminates the need for a conventional ignition key and mechanical steering column switch. Security is provided by the smart fob, which uses a programmed ID code or rolling ID code to communicate with the vehicle’s anti-theft system. It’s no different than a conventional ignition key with an electronic chip communicating with the anti-theft system before the engine can be started.
The keyless smart fob is detected by one or more antennas located on the vehicle. The only difference is that the keyless push button start systems do more than just unlock the doors. Once the fob is used to unlock the door and/or is inside the vehicle, it’s the same as if the driver has inserted a key into the ignition switch and turned it to the “on” position. The smart fob transponder broadcasts its ID code to the keyless entry immobilizer module, which then authenticates the code.
The engine won’t start automatically for obvious safety reasons (same for energizing a hybrid-drive system), so nothing happens until the driver presses the Start button and issues a start command. When the start command is received via a hard-wired circuit to the PCM or the CAN communication bus, the PCM energizes the fuel and ignition systems, and current is routed to the starter to crank the engine.
An electronic steering lock is also released to unlock the steering column, and a signal is sent to the transmission controller (if separate from the PCM) to allow the transmission to be shifted out of Park.
Most systems require the same safety precautions as a conventional starting system. The transmission must be in Park (or Neutral) before the engine can be started, and the driver must depress and hold the brake pedal (or clutch pedal).

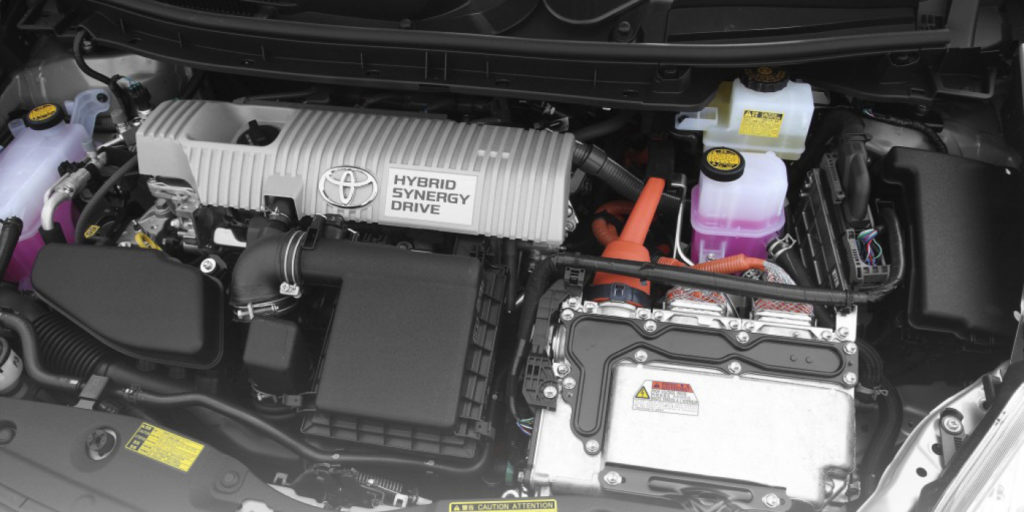
In the case of a hybrid application like a Toyota Prius, pushing the Power button tells the hybrid system controller that the driver is ready to go. The “Ready” light comes on telling the driver the transmission can now be placed in Drive or Reverse, and the car is ready to go.
On many vehicles, there is a receptacle in the dash for the smart fob. The receptacle’s purpose is to hold the fob so it doesn’t roll around inside the car, and to recognize and authenticate the smart fob ID code.
One misconception motorists have about the receptacle is that it recharges the fob. It does not. Most smart fobs use a small 3.0-volt lithium button battery for power. The battery powers the keyless entry transponder that sends out a coded signal to unlock or lock the doors, and to deactivate or activate the anti-theft system. Once the fob is inside the vehicle, or is placed into the dash receptacle, it’s mostly passive and uses minimal power to activate its transponder.
The battery inside the fob should usually last several years. Lithium batteries are not rechargeable, so when they eventually run down, the fob has to be pried open so the battery can be replaced. Always refer to the vehicle service information or owner’s manual for the type of battery required, and the proper procedure for replacing the battery. Figuring out how to open a fob isn’t always obvious, and if you use the wrong technique or brute force to pry it open, you’ll probably break it.