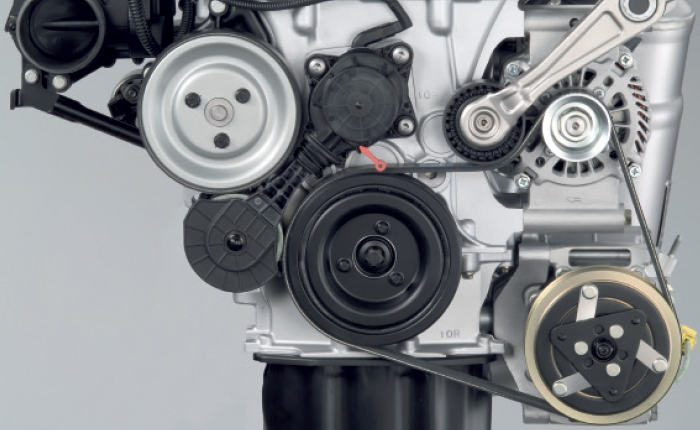
One of the more interesting drive belt arrangements can be found on the MINI Cooper with the 1.6L Tritec engine. The new four-cylinder engine had a surprise for technicians when it came time to replace the water pump.
The water pump has what looks to be a belt around the pulley, but it’s actually rubber bonded to the outside. The water pump is turned by a metal wheel driven by the crankshaft pulley – this wheel is what transfers the motion of the crankshaft to the water pump.
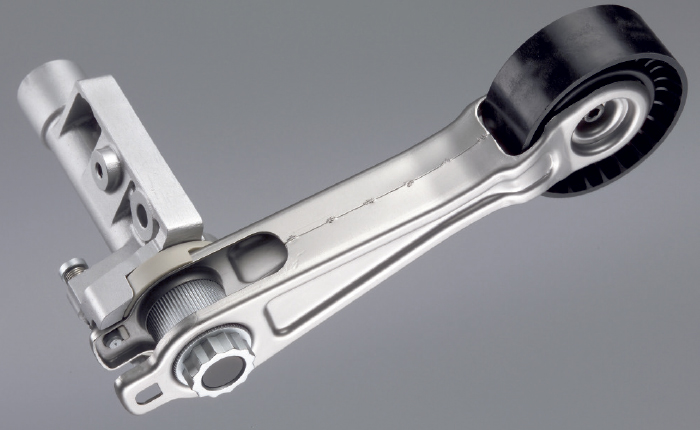
This innovative tensioner is called a friction wheel drive system. The tensioner is able to disengage the water pump until the engine has reached a specific temperature. On a cold engine that is turned off, the tensioner will feel a little loose and you might be able to turn the pump by hand.
When the engine management system engages the water pump a small electric motor inside the tensioner changes the length of tensioner. The wheel is pulled onto the back of the belt on the crankshaft and water pump pulley.
If you need to replace the belt or water pump, you need to disengage the tensioner. To release the tension, a tab first needs to be pulled out. The main problem that can occur is the rubber on the outside of the water pump can wear out or come off the wheel. This can cause noise and possible damage to the tensioner and even to the back of the drive belt. If the water pump or wheel on the tensioner seizes, it can cause a flat spot on the pulley and can also cause damage to the drive belt. Some aftermarket suppliers have improved the rubber on the pulley so it will not separate.
Check the movement of the tensioner arm with the engine off. Use a socket with a long-handled ratchet or breaker bar on the tensioner pulley center bolt to rotate the tensioner. There are no specifications for measuring the amount of resistance offered by the tensioner spring, but if the tensioner offers little resistance, it may indicate a weak or broken spring. If it fails to move at all, the tensioner is jammed and needs to be replaced.
Note the wear pattern on the tensioner and idler pulley(s). Misalignment and bearing wear can cause the belt to track off-center. This will cause the belt to wear quickly. The tensioner and idler pulley bearings can be checked by removing the belt and spinning the pulleys by hand. All pulleys should turn freely with no binding, roughness or wobble. Any binding, roughness or wobble means these parts are bad and need to be replaced.
Also, note the position of the arm on the automatic tensioner. Many units have marks on the housing that show the normal range in which the arm can pivot. If the position of the arm is outside these marks, it indicates a problem (the belt may be too long or too short, or the tensioner may be jammed).
Watch the belt while the engine is running. If you see a lot of movement or flutter in the belt, the tensioner is probably weak or sticking and should be replaced. Many tensioners also have an indicator mark that shows its range of travel. If the mark is not within the normal limits, the tensioner is weak or sticking, or the belt is not the correct length for the application.
The tensioner also provides a little “give” so it can absorb and cushion shock loads on the belt that occur when the A/C compressor clutch cycles on and off. What’s more, the tensioner automatically compensates for wear and keeps the belt under constant tension. But, nothing lasts forever – not belts and not automatic tensioners.
An engineer could design a belt system that would never slip or wear out. But the power required to turn the components would require a lot of extra fuel that would hurt the fuel economy. If a BMW engineer designs a system that requires minimal power, the belt might slip and wear prematurely.
The tension of the belt is another engineering equation that must be balanced with the amount of belt contact on a pulley. If the tension is too great, it will cause increased load on the engine and damage due to the side loads on the components. If there is not enough tension, the belt will slip.
Poor alignment is the number one cause of belt noise. Poor alignment can also cause premature wear, belt mistracking or rib skipping, and belt edge wear and fraying. Sight down the side of the belt to make sure the edge does not make any bends toward or away from the engine. Any deviation you can detect with your eye is too much.
Try to move the pulleys fore and aft to make sure the mounting is tight and the pulley exhibits minimal axial movement, which can cause misalignment. With your hands, move all idlers fore and aft and check for free rock. Excessive movement indicates a bearing or alignment problem and that the idler should be replaced.