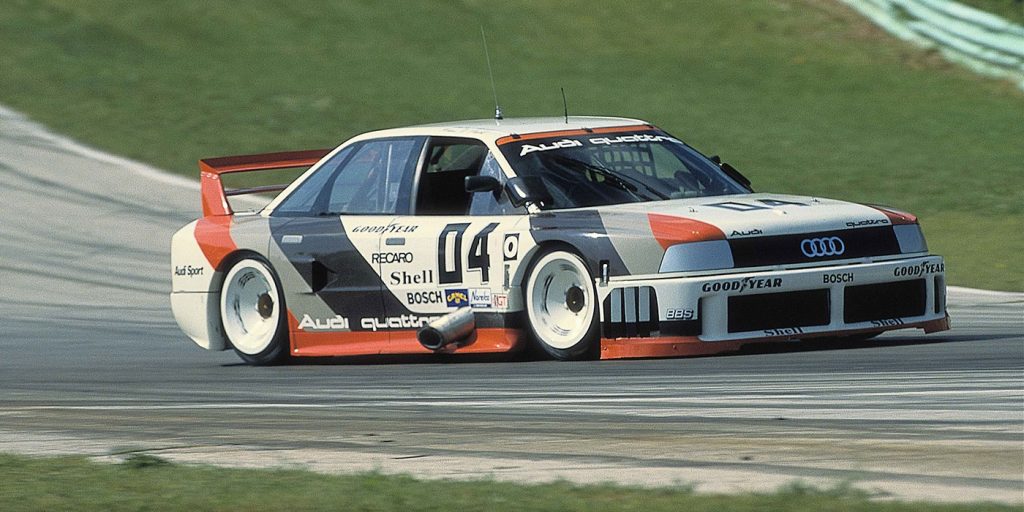
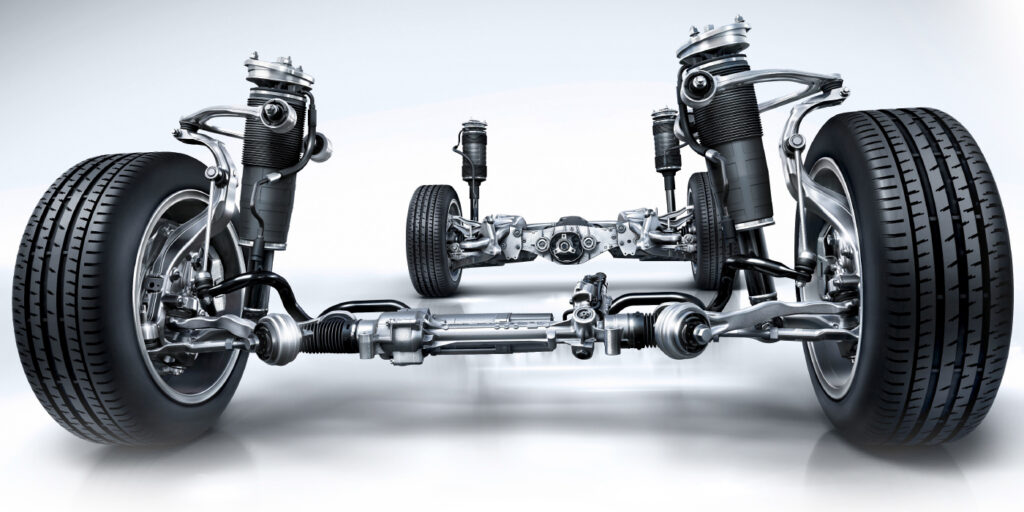
The Audi Quattro drivetrain has built up an impressive track record for over 40 years. In 2019, Audi had produced 10,448,406 cars with all-wheel drive, including 804,224 in 2019 alone. Almost 45% of all Audi models built in 2019 featured Quattro drive systems.
The first Quattro system was revolutionary. The transmission was first designed to be front-wheel drive only. The engineers figured out how to make a hollow output shaft. Inside the output shaft is a secondary shaft that can carry power to the front and rear of the transmission. From its rear end, it drove the housing of the center differential, which was configured as a manually locking bevel-gear differential. In normal situations, it sent 50% of the power along with the driveshaft to the rear axle, which was equipped with a second locking differential.
The first systems had locking differentials the driver could control. In 1986, the Quattro system received a Torsen center differential. In 1999, some models received a viscous coupling. Since the mid-2000s, many models have crown gear center differential. At the front and rear differentials, electrically actuated clutches work with the center differential and stability control system to send power to the wheel that needs it.
As the Quattro system has evolved, so have the controls for the front, rear and center differential systems. Early systems used engine vacuum to lock the differentials. Later models used hydraulic fluid and solenoids to control the differentials. Now, the differentials are controlled with clutches to vector the torque.
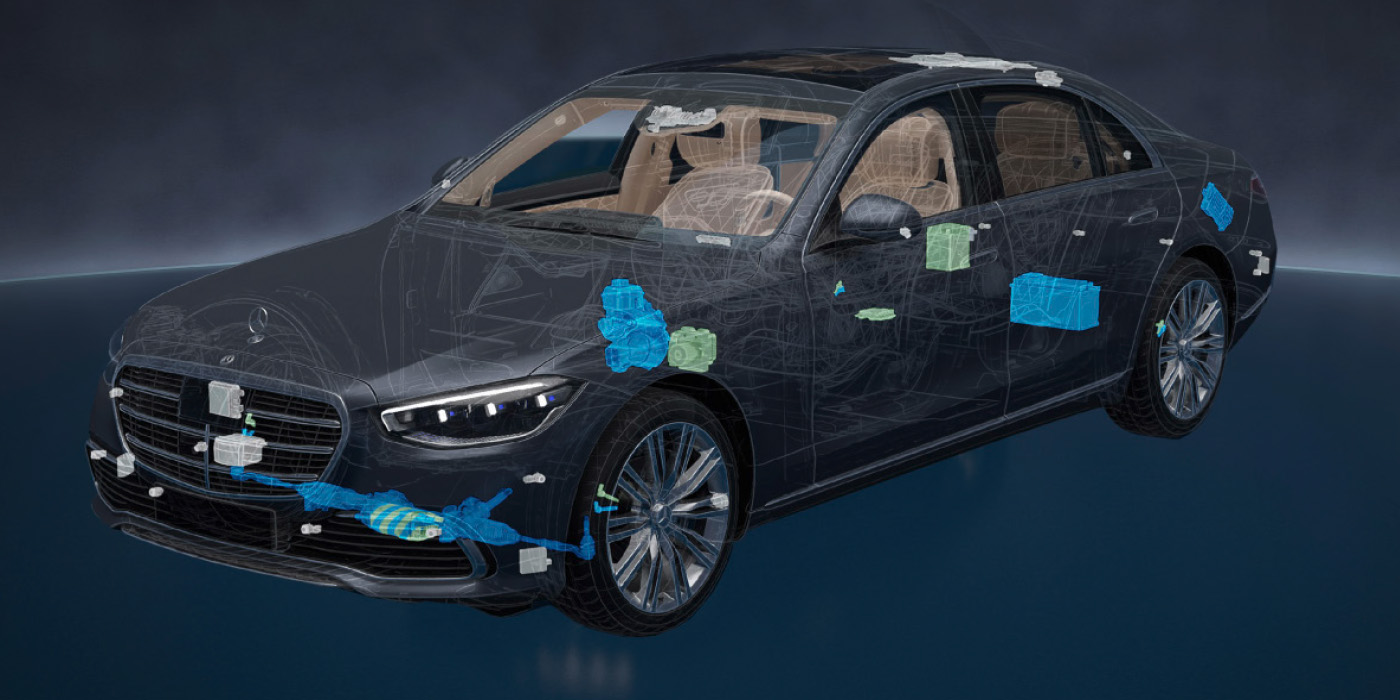
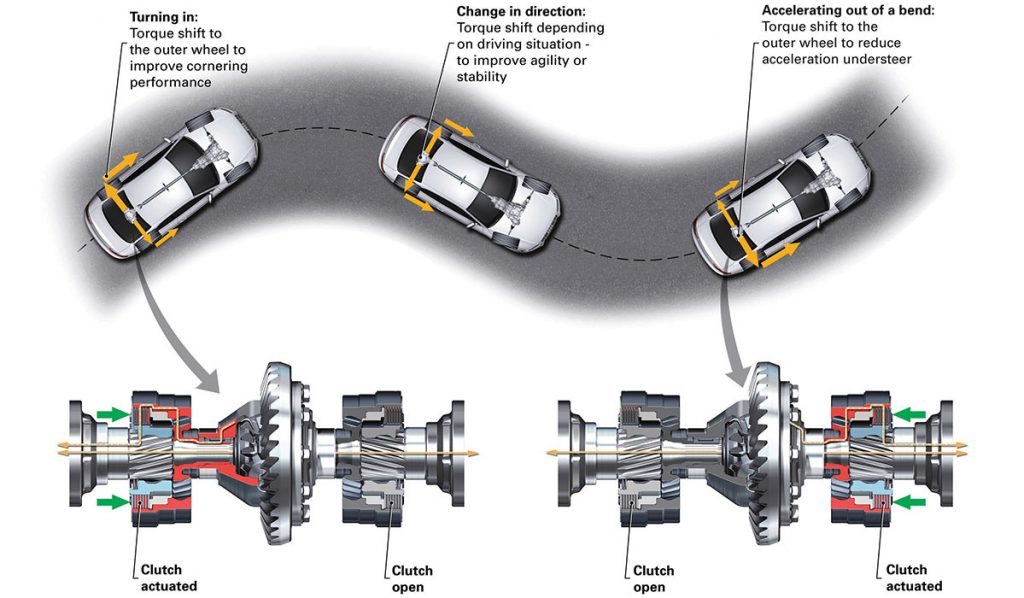
The all-wheel-drive control module continuously calculates the best torque distribution between the front and rear axles based on extensive data. When the requirements change, the electric axial piston pump builds up as much as 650 psi of hydraulic pressure within just a few milliseconds. It presses the friction plates together, which enables variable transmission of the drive torque from the front axle to the rear.
The water-cooled multi-plate clutch in the center differential distributes the necessary torque to the front wheels in any driving situation, is integrated within this. There is no fixed basic distribution; in extreme cases, up to 100% can be transmitted to the front or rear axle.
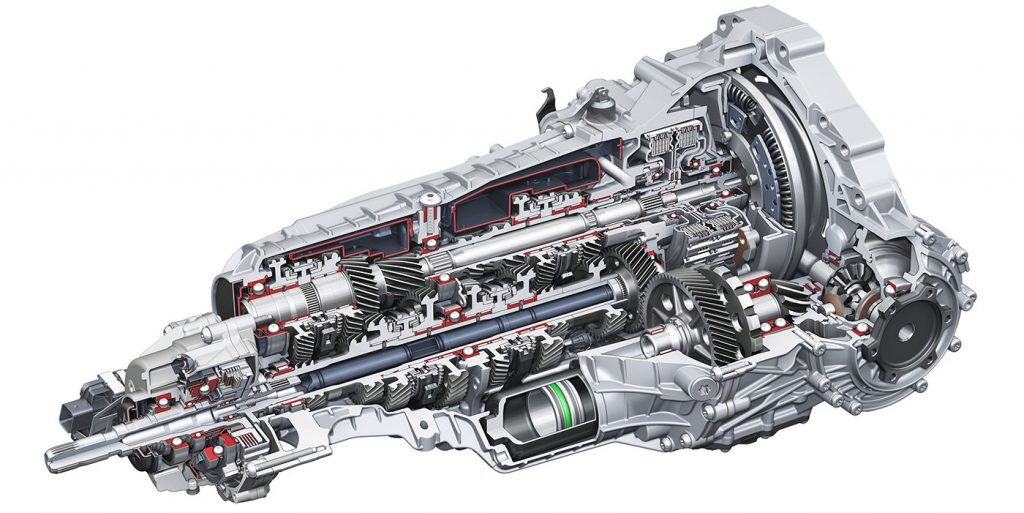
The layout of the Quattro transmission has changed over the years and for different models. Most late-model Audi cars with a longitudinal-mounted engine have moved the center differential to the rear of the transmission. The front differential or driveshaft on some is no longer inside the transmission.
Since Audi has been sharing platforms with VWs that have a transversely mounted engine like the TT and A3, the Haldex system has made its way to Audi. The Haldex coupling is mounted on the rear axle differential and is driven by the drive shaft. Engine torque is transmitted to the drive shaft through the gearbox, the front axle differential, and the front axle drive.
The driveshaft is connected to the input shaft of the Haldex coupling. In the Haldex coupling, the input shaft is separated from the output shaft to the rear axle differential. Torque can only be transmitted to the rear axle differential when the Haldex coupling clutch plates are engaged.
Maintenance
With most late-model Audi differentials, there might not be a replacement interval for the fluid inside the case. In the service schedule, it is recommended the fluid is inspected every other oil change or every 20,000 miles. It can be impossible to observe the condition of the fluid. But if the axle or shaft seals are leaking, the fluid needs to be replaced and the seal fixed. For Haldex- equipped vehicles, the clutch fluid needs to be replaced every 35,000 miles.
Audi Quattro vehicles can come with manual, automatic or dual-clutch (DSG) transmissions. The fluid maintenance intervals for transmissions can vary. The DSG requires fluid replacement every 35,000 miles.