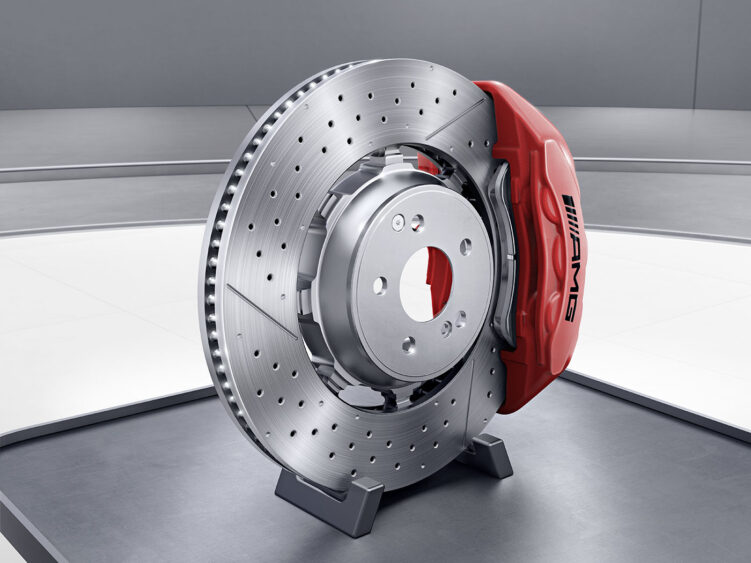
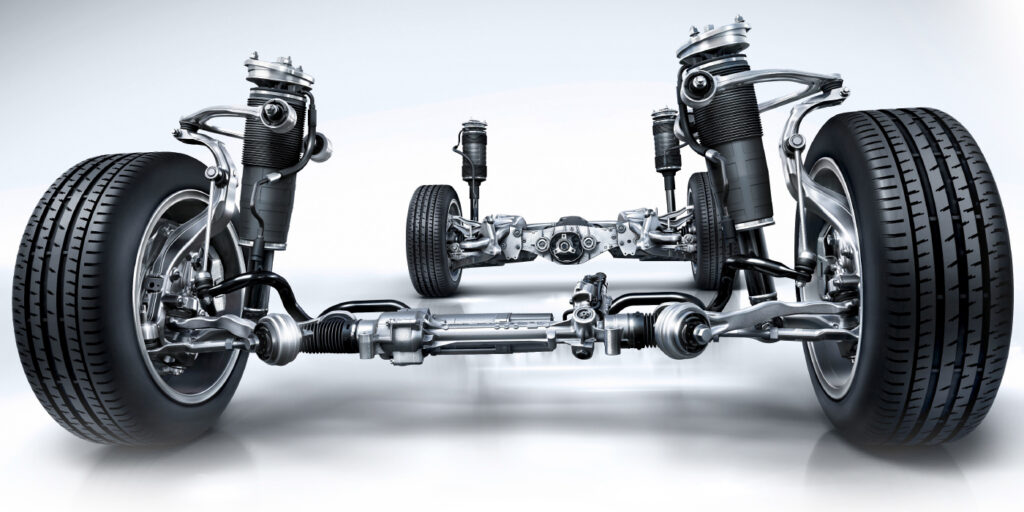
When you hear the words “floating rotor,” you might think of a racecar brake rotor with Allen head bolts holding the hat to the outer ring. But, more economical and robust “semi-floating” rotors have made it onto Audi, BMW and Mercedes-Benz daily drivers.
A semi-floating, dual-cast or composite rotor has two advantages over a fully cast rotor. First, these rotors weigh less. The weight savings increase fuel economy while improving braking and handling performance since the unsprung mass is reduced.
Second, this rotor design allows the outer ring to expand and contract at a different rate than the hat, which can help prevent cracking on rotors that have diameters larger than 12 inches. This is why the BMW M5 and M6 can have rotors that are more than 15 inches in diameter in the front and rear.
Types of Rotors
Current composite or floating rotor designs use a cast-iron ring mated to a forged aluminum hat. Since it is almost impossible to weld cast iron to aluminum, two methods to mechanically fasten the rotor to the hat are being used by Audi, BMW and Mercedes-Benz.
Audi and BMW attach the hat to the outer ring using pins that go through the side of the hat and into the rotor. These are pressed in with extreme force. The heads of the pin can be seen through the wheels.
BMW TSB SI B34 05 15 discusses customer complaints of a ticking noise coming from the front wheels while cornering at slow speeds and during parking. This condition is caused by movement between the inner contact surfaces of the brake rotor and the flange. The solution is P/N 31 10 8 053 073 — a “friction washer” that fits between the flange and rotor.
On some mid-line Mercedes-Benz AMG vehicles, the company opted to use a design from a supplier that makes composite rotors for Maserati, GM and other manufacturers. This design utilizes an aluminum hat section; the hat has projections that go into the rotor around which the iron forms while the casting is spun.
Serviceability
Veteran technicians will remember the problems some domestic and import vehicles with composite rotors had in the late 1990s. These rotors had hats made of stamped steel that were cast into the iron rotor. They were prone to lateral runout due to installation errors.
The same is true for the new generation of composite rotors. If a technician tightens the lug nuts unevenly or with too much torque, runout could be induced. This runout typically results in pedal pulsation in 6,000 miles or less.
The bad news is that some of these rotors can’t be machined because of their design. On some applications, the front rotors allow for only 2 mm of wear before they are below the discard measurement. It is critical to check your service information for recommendations to measure and machine these types of rotors.